Aberrant Bcl-x splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation
- PMID: 34118966
- PMCID: PMC8196531
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02001-w
Aberrant Bcl-x splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation
Abstract
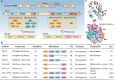
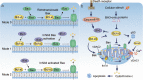
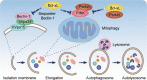
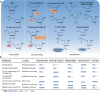
Bcl-x pre-mRNA splicing serves as a typical example to study the impact of alternative splicing in the modulation of cell death. Dysregulation of Bcl-x apoptotic isoforms caused by precarious equilibrium splicing is implicated in genesis and development of multiple human diseases, especially cancers. Exploring the mechanism of Bcl-x splicing and regulation has provided insight into the development of drugs that could contribute to sensitivity of cancer cells to death. On this basis, we review the multiple splicing patterns and structural characteristics of Bcl-x. Additionally, we outline the cis-regulatory elements, trans-acting factors as well as epigenetic modifications involved in the splicing regulation of Bcl-x. Furthermore, this review highlights aberrant splicing of Bcl-x involved in apoptosis evade, autophagy, metastasis, and therapy resistance of various cancer cells. Last, emphasis is given to the clinical role of targeting Bcl-x splicing correction in human cancer based on the splice-switching oligonucleotides, small molecular modulators and BH3 mimetics. Thus, it is highlighting significance of aberrant splicing isoforms of Bcl-x as targets for cancer therapy.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; Bcl-x; Cell apoptosis; Small molecular modulators; Splice-switching oligonucleotides; Splicing correction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modification of BCLX pre-mRNA splicing has antitumor efficacy alone or in combination with radiotherapy in human glioblastoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 21;15(2):160. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06507-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38383492 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic effects of splice-switching oligonucleotides targeting Bcl-x pre-mRNA in human glioma cell lines.Oncol Rep. 2016 Feb;35(2):1013-9. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4465. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 26718027
-
Antagonistic effects of the SRp30c protein and cryptic 5' splice sites on the alternative splicing of the apoptotic regulator Bcl-x.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 1;283(31):21315-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800353200. Epub 2008 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18534987
-
Aberrant Cyclin D1 splicing in cancer: from molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Apr 6;14(4):244. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05763-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37024471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Splice variants in apoptotic pathway.Exp Oncol. 2012 Oct;34(3):212-7. Exp Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23070006 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing of BCL-x is controlled by RBM25 binding to a G-quadruplex in BCL-x pre-mRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Nov 10;51(20):11239-11257. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad772. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37811881 Free PMC article.
-
Using deep long-read RNAseq in Alzheimer's disease brain to assess medical relevance of RNA isoform diversity.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 11:2023.08.06.552162. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.06.552162. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;43(4):635-646. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02245-9. PMID: 37609156 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Protein isoform-centric therapeutics: expanding targets and increasing specificity.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Oct;23(10):759-779. doi: 10.1038/s41573-024-01025-z. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39232238 Review.
-
Mapping medically relevant RNA isoform diversity in the aged human frontal cortex with deep long-read RNA-seq.Nat Biotechnol. 2025 Apr;43(4):635-646. doi: 10.1038/s41587-024-02245-9. Epub 2024 May 22. Nat Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38778214 Free PMC article.
-
Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy: focusing on alternative splicing.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1437774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437774. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39055714 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

