The biogenesis and biological function of PIWI-interacting RNA in cancer
- PMID: 34118972
- PMCID: PMC8199808
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-021-01104-3
The biogenesis and biological function of PIWI-interacting RNA in cancer
Abstract
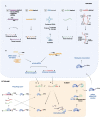
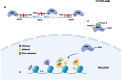
Small non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are vital regulators of biological activities, and aberrant levels of small ncRNAs are commonly found in precancerous lesions and cancer. PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) are a novel type of small ncRNA initially discovered in germ cells that have a specific length (24-31 nucleotides), bind to PIWI proteins, and show 2'-O-methyl modification at the 3'-end. Numerous studies have revealed that piRNAs can play important roles in tumorigenesis via multiple biological regulatory mechanisms, including silencing transcriptional and posttranscriptional gene processes and accelerating multiprotein interactions. piRNAs are emerging players in the malignant transformation of normal cells and participate in the regulation of cancer hallmarks. Most of the specific cancer hallmarks regulated by piRNAs are involved in sustaining proliferative signaling, resistance to cell death or apoptosis, and activation of invasion and metastasis. Additionally, piRNAs have been used as biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis and have great potential for clinical utility. However, research on the underlying mechanisms of piRNAs in cancer is limited. Here, we systematically reviewed recent advances in the biogenesis and biological functions of piRNAs and relevant bioinformatics databases with the aim of providing insights into cancer diagnosis and clinical applications. We also focused on some cancer hallmarks rarely reported to be related to piRNAs, which can promote in-depth research of piRNAs in molecular biology and facilitate their clinical translation into cancer treatment.
Keywords: Biogenesis; Biomarker; Cancer hallmarks; Database; piRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel dimensions of piRNAs in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 Aug 9;336(1):46-52. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 16. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23603435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) and cancer: Emerging biological concepts and potential clinical implications.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019 Jan;1871(1):160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 30. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30599187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of the piRNA/piwi complex in cancer.Mol Cancer. 2019 Aug 9;18(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1052-9. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31399034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIWI Proteins and PIWI-Interacting RNA: Emerging Roles in Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(1):1-20. doi: 10.1159/000484541. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29130960 Review.
-
PIWI-interacting RNAs: Critical roles and therapeutic targets in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2023 May 28;562:216189. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216189. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 37076042 Review.
Cited by
-
Small Noncoding RNAome Changes During Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Senescence In Vitro.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 13;13:808223. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.808223. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35634512 Free PMC article.
-
piRNA-1742 promotes renal cell carcinoma malignancy by regulating USP8 stability through binding to hnRNPU and thereby inhibiting MUC12 ubiquitination.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Jun;55(6):1258-1271. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01010-3. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37332045 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sphingolipids in Multiple Myeloma Progression, Drug Resistance, and Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 8;12:925807. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.925807. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35756630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iPiDA-LGE: a local and global graph ensemble learning framework for identifying piRNA-disease associations.BMC Biol. 2025 May 9;23(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02221-y. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40346532 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA Contribution to Aging and Lifespan.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;79(4):glae058. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glae058. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38394352 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

