Severe COVID-19 in Alzheimer's disease: APOE4's fault again?
- PMID: 34118974
- PMCID: PMC8197596
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-021-00858-9
Severe COVID-19 in Alzheimer's disease: APOE4's fault again?
Abstract
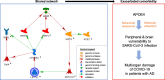
Challenges have been recognized in healthcare of patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) in the COVID-19 pandemic, given a high infection and mortality rate of COVID-19 in these patients. This situation urges the identification of underlying risks and preferably biomarkers for evidence-based, more effective healthcare. Towards this goal, current literature review and network analysis synthesize available information on the AD-related gene APOE into four lines of mechanistic evidence. At a cellular level, the risk isoform APOE4 confers high infectivity by the underlying coronavirus SARS-CoV-2; at a genetic level, APOE4 is associated with severe COVID-19; at a pathway level, networking connects APOE with COVID-19 risk factors such as ACE2, TMPRSS2, NRP1, and LZTFL1; at a behavioral level, APOE4-associated dementia may increase the exposure to coronavirus infection which causes COVID-19. Thus, APOE4 could exert multiple actions for high infection and mortality rates of the patients, or generally, with COVID-19.
Keywords: APOE4; Biomarker; COVID-19; Comorbidity; Coronavirus; Peripheral mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
APOE4: A Culprit for the Vulnerability of COVID-19 in Alzheimer's Patients.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023;20(1):162-169. doi: 10.2174/1567202620666230202140612. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 36733199 Review.
-
APOE interacts with ACE2 inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry and inflammation in COVID-19 patients.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 1;7(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01118-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35915083 Free PMC article.
-
ApoE4 associated with severe COVID-19 outcomes via downregulation of ACE2 and imbalanced RAS pathway.J Transl Med. 2023 Feb 9;21(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03945-7. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36759834 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of apolipoprotein E4 (ApoE4) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: lessons from ApoE mouse models.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Aug;39(4):924-32. doi: 10.1042/BST0390924. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21787325
-
Relation between Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's Disease and SARS-CoV-2 and their Treatment Strategy: A Review.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(1):9-20. doi: 10.2174/1871527322666221226145141. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 36573058 Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's Disease and Toxins Produced by Marine Dinoflagellates: An Issue to Explore.Mar Drugs. 2022 Apr 2;20(4):253. doi: 10.3390/md20040253. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35447926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APOE ε4 associates with increased risk of severe COVID-19, cerebral microhaemorrhages and post-COVID mental fatigue: a Finnish biobank, autopsy and clinical study.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021 Dec 23;9(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01302-7. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2021. PMID: 34949230 Free PMC article.
-
Externalizing traits: Shared causalities for COVID-19 and Alzheimer's dementia using Mendelian randomization analysis.PNAS Nexus. 2023 Jun 15;2(6):pgad198. doi: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgad198. eCollection 2023 Jun. PNAS Nexus. 2023. PMID: 37361546 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mortality rate in memory clinic patients.Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024 Jan 28;16(1):e12541. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12541. eCollection 2024 Jan-Mar. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2024. PMID: 38288266 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive impairment in long-COVID and its association with persistent dysregulation in inflammatory markers.Front Immunol. 2023 May 23;14:1174020. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1174020. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37287969 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

