Integrin α2β1-targeting ferritin nanocarrier traverses the blood-brain barrier for effective glioma chemotherapy
- PMID: 34120610
- PMCID: PMC8201891
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-00925-1
Integrin α2β1-targeting ferritin nanocarrier traverses the blood-brain barrier for effective glioma chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Ferritin, the natural iron storage protein complex, self-assembles into a uniform cage-like structure. Human H-ferritin (HFn) has been shown to transverse the blood-brain barrier (BBB) by binding to transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1), which is abundant in endothelial cells and overexpressed in tumors, and enters cells via endocytosis. Ferritin is easily genetically modified with various functional molecules, justifying that it possesses great potential for development into a nanocarrier drug delivery system.
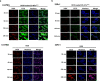
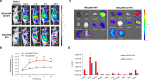
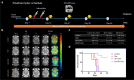
Results: In this study, a unique integrin α2β1-targeting H-ferritin (2D-HFn)-based drug delivery system was developed that highlights the feasibility of receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT) for glioma tumor treatment. The integrin targeting α2β1 specificity was validated by biolayer interferometry in real time monitoring and followed by cell binding, chemo-drug encapsulation stability studies. Compared with naïve HFn, 2D-HFn dramatically elevated not only doxorubicin (DOX) drug loading capacity (up to 458 drug molecules/protein cage) but also tumor targeting capability after crossing BBB in an in vitro transcytosis assay (twofold) and an in vivo orthotopic glioma model. Most importantly, DOX-loaded 2D-HFn significantly suppressed subcutaneous and orthotopic U-87MG tumor progression; in particular, orthotopic glioma mice survived for more than 80 days.
Conclusions: We believe that this versatile nanoparticle has established a proof-of-concept platform to enable more accurate brain tumor targeting and precision treatment arrangements. Additionally, this unique RMT based ferritin drug delivery technique would accelerate the clinical development of an innovative drug delivery strategy for central nervous system diseases with limited side effects in translational medicine.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Ferritin; Integrin α2β1; Receptor-mediated transcytosis (RMT); Transferrin receptor 1.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Ferritin Nanocarrier Traverses the Blood Brain Barrier and Kills Glioma.ACS Nano. 2018 May 22;12(5):4105-4115. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b06969. Epub 2018 Apr 4. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 29608290
-
Rational design of engineered H-ferritin nanoparticles with improved siRNA delivery efficacy across an in vitro model of the mouse BBB.Nanoscale. 2022 May 5;14(17):6449-6464. doi: 10.1039/d1nr07880a. Nanoscale. 2022. PMID: 35416195
-
Target delivering paclitaxel by ferritin heavy chain nanocages for glioma treatment.J Control Release. 2020 Jul 10;323:191-202. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.010. Epub 2019 Dec 12. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 31838201
-
Ferritin: A Multifunctional Nanoplatform for Biological Detection, Imaging Diagnosis, and Drug Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Sep 7;54(17):3313-3325. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00267. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34415728 Review.
-
Ferritin nanoparticles: new strategies for the diagnosis and treatment of central nervous system diseases.Biomed Mater. 2025 Feb 6;20(2). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/adab5a. Biomed Mater. 2025. PMID: 39820046 Review.
Cited by
-
Customizing delivery nano-vehicles for precise brain tumor therapy.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Jan 28;21(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01775-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36707835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-Based Nanoparticles for the Imaging and Treatment of Solid Tumors: The Case of Ferritin Nanocages, a Narrative Review.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 25;13(12):2000. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122000. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and application of ferritin-based nanomedicine for targeted cancer therapy.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025 Mar;20(5):481-500. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2025.2459056. Epub 2025 Feb 3. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39895329 Review.
-
Nanocarriers for targeted drug delivery in the vascular system: focus on endothelium.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 12;22(1):620. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02892-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39396002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferritin-based disruptor nanoparticles: A novel strategy to enhance LDL cholesterol clearance via multivalent inhibition of PCSK9-LDL receptor interaction.Protein Sci. 2024 Sep;33(9):e5111. doi: 10.1002/pro.5111. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39150051 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer.
-
- Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M, Xia Y. Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2014;53:12320–12364. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

