A critical relationship between bone and fat: the role of bone marrow adipose-derived RANKL in bone metabolism
- PMID: 34121307
- PMCID: PMC8256289
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202152986
A critical relationship between bone and fat: the role of bone marrow adipose-derived RANKL in bone metabolism
Abstract
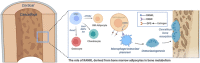
Recent studies have unveiled unique functions of the bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT), which represent over 10% of the total adipose tissue mass in healthy adults. Increasing evidence is emerging as to how BMAT deposition and osteoporosis are linked under normal and pathophysiological conditions, which is opening up novel treatment avenues. However, the means by which bone marrow adipocytes (BMAs) regulate bone remodeling and their involvement in osteoporosis remained unknown. A study in this issue of EMBO Reports (Hu et al, 2021) and a study in Journal of Clinical Investigation (Yu et al, 2021) reports independently that BMA-derived RANKL regulates osteoclastogenesis and bone remodeling, indicating that excessive RANKL generated by BMAs is an underlying cause for osteoporosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY NC ND 4.0 license.
Figures
Comment on
-
Bone marrow adipogenic lineage precursors promote osteoclastogenesis in bone remodeling and pathologic bone loss.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jan 19;131(2):e140214. doi: 10.1172/JCI140214. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33206630 Free PMC article.
-
RANKL from bone marrow adipose lineage cells promotes osteoclast formation and bone loss.EMBO Rep. 2021 Jul 5;22(7):e52481. doi: 10.15252/embr.202152481. Epub 2021 Jun 13. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 34121311 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berner HS, Lyngstadaas SP, Spahr A, Monjo M, Thommesen L, Drevon CA, Syversen U, Reseland JE (2004) Adiponectin and its receptors are expressed in bone‐forming cells. Bone 35: 842–849 - PubMed
-
- Mukohira H, Hara T, Abe S, Tani‐Ichi S, Sehara‐Fujisawa A, Nagasawa T, Tobe K, Ikuta K (2019) Mesenchymal stromal cells in bone marrow express adiponectin and are efficiently targeted by an adiponectin promoter‐driven Cre transgene. Int Immunol 31: 729–742 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

