Comparative efficacy of lemborexant and other insomnia treatments: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 34121443
- PMCID: PMC10394202
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.21011
Comparative efficacy of lemborexant and other insomnia treatments: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
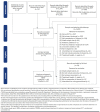
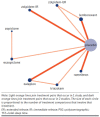
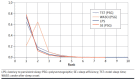
BACKGROUND: Insomnia is a common disorder associated with a substantial burden of illness, particularly in older adults. OBJECTIVE: To compare the efficacy and safety of lemborexant with specified other insomnia treatments through a systematic literature review and network meta-analysis (NMA). METHODS: Medline and Embase were systematically searched from inception to February 2019 and updated with a targeted search of PubMed for pivotal trials in March 2021. Randomized controlled trials in adults with primary insomnia were included if they reported results following at least 1 week of treatment. Interventions of interest were specified as lemborexant, suvorexant, benzodiazepines, benzodiazepine receptor agonists (also called Z-drugs [zolpidem, eszopiclone, zaleplon, zopiclone]), trazodone, and ramelteon. Efficacy outcomes included wake after sleep onset (WASO), sleep efficiency (SE), latency to persistent sleep (LPS)/sleep onset latency (SOL), total sleep time (TST) and Insomnia Severity Index (ISI). Bayesian NMA were performed at predetermined time intervals approximating 4 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months. Safety outcomes included serious adverse events (SAEs), withdrawals due to adverse events (AEs), and specified AEs (dizziness, somnolence, and falls). Subgroup analysis was conducted in the older population. RESULTS: 45 studies were included in the NMA. At 4 weeks, lemborexant had the highest probability of being the best treatment for 3 of the 4 outcomes measured objectively by polysomnography-TST, LPS, and SE-and was ranked second to suvorexant on WASO. Eszopiclone was highly ranked for subjectively measured SOL and ISI at 4 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months. Lemborexant was rated more highly than suvorexant in subjective measures of WASO, TST, and SOL at 4 weeks (the differences were not statistically significant). No statistically significant interactions between treatment effect and older subpopulations were found, indicating that the treatment effect was similar in older and adult populations. The safety profile of lemborexant was broadly similar to the other treatments for SAEs and withdrawals due to AEs. A limitation is the age of some of the included studies (3 were published in 1990 or earlier). A further limitation is the lack of stratification of recommended doses. If the doses used in the study publications do not reflect doses used in clinical practice, this could potentially bias the results. CONCLUSIONS: Lemborexant was ranked highest of the treatments studied on 3 out of the 4 objectively measured insomnia efficacy outcomes, with a safety profile broadly similar to other insomnia treatments. DISCLOSURES: This work was funded by Eisai Inc., which was involved with all stages of the study and analysis. McElroy, O'Leary, and Adena are consultants with Datalytics Pty Ltd., which was paid by Eisai Inc. for conducting the literature review and analysis. They were not financially compensated for collaborative efforts on publication-related activities. Campbell, Tahami Monfared, and Meier are employed by Eisai Inc. This study was presented as a poster at AMCP Nexus Virtual, October 20-23, 2020 and at the AGS Virtual Annual Scientific Meeting 2021, May 13-15, 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by Eisai Inc., which was involved with all stages of the study and analysis. McElroy, O’Leary, and Adena are consultants with Datalytics Pty Ltd., which was paid by Eisai Inc. for conducting the literature review and analysis. They were not financially compensated for collaborative efforts on publication-related activities. Campbell, Tahami Monfared, and Meier are employed by Eisai Inc.
This study was presented as a poster at AMCP Nexus Virtual, October 20-23, 2020 and at the AGS Virtual Annual Scientific Meeting 2021, May 13-15, 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Roth T, Coulouvrat C, Hajak G, et al. . Prevalence and perceived health associated with insomnia based on DSM-IV-TR; International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision; and Research Diagnostic Criteria/International Classification of Sleep Disorders, Second Edition criteria: results from the America Insomnia Survey. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69(6):592-600. - PubMed
-
- Olfson M, Wall M, Liu SM, Morin CM, Blanco C. Insomnia and impaired quality of life in the United States. J Clin Psychiatry. 2018;79(5):17m12020. - PubMed
-
- Lombardi DA, Folkard S, Willetts JL, Smith GS. Daily sleep, weekly working hours, and risk of work-related injury: US National Health Interview Survey (2004-2008). Chronobiol Int. 2010;27(5):1013-30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical