Synaptic Remodeling in the Cone Pathway After Early Postnatal Horizontal Cell Ablation
- PMID: 34122012
- PMCID: PMC8187617
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.657594
Synaptic Remodeling in the Cone Pathway After Early Postnatal Horizontal Cell Ablation
Abstract
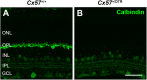
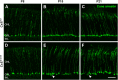
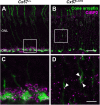
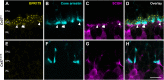
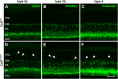
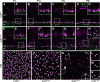
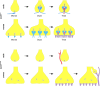
The first synapse of the visual pathway is formed by photoreceptors, horizontal cells and bipolar cells. While ON bipolar cells invaginate into the photoreceptor terminal and form synaptic triads together with invaginating horizontal cell processes, OFF bipolar cells make flat contacts at the base of the terminal. When horizontal cells are ablated during retina development, no invaginating synapses are formed in rod photoreceptors. However, how cone photoreceptors and their synaptic connections with bipolar cells react to this insult, is unclear so far. To answer this question, we specifically ablated horizontal cells from the developing mouse retina. Following ablation around postnatal day 4 (P4)/P5, cones initially exhibited a normal morphology and formed flat contacts with OFF bipolar cells, but only few invaginating contacts with ON bipolar cells. From P15 on, synaptic remodeling became obvious with clustering of cone terminals and mislocalized cone somata in the OPL. Adult cones (P56) finally displayed highly branched axons with numerous terminals which contained ribbons and vesicular glutamate transporters. Furthermore, type 3a, 3b, and 4 OFF bipolar cell dendrites sprouted into the outer nuclear layer and even expressed glutamate receptors at the base of newly formed cone terminals. These results indicate that cones may be able to form new synapses with OFF bipolar cells in adult mice. In contrast, cone terminals lost their invaginating contacts with ON bipolar cells, highlighting the importance of horizontal cells for synapse maintenance. Taken together, our data demonstrate that early postnatal horizontal cell ablation leads to differential remodeling in the cone pathway: whereas synapses between cones and ON bipolar cells were lost, new putative synapses were established between cones and OFF bipolar cells. These results suggest that synapse formation and maintenance are regulated very differently between flat and invaginating contacts at cone terminals.
Keywords: bipolar cells; cones; horizontal cells; photoreceptors; retina; ribbon synapse; synaptic remodeling; vision.
Copyright © 2021 Nemitz, Dedek and Janssen-Bienhold.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The synaptic ultrastructure in the outer plexiform layer of the catfish retina: a three-dimensional study with HVEM and conventional EM of Golgi-impregnated bipolar and horizontal cells.J Comp Neurol. 1986 May 8;247(2):181-99. doi: 10.1002/cne.902470205. J Comp Neurol. 1986. PMID: 2424939
-
The absence of functional bassoon at cone photoreceptor ribbon synapses affects signal transmission at Off cone bipolar cell contacts in mouse retina.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021 Mar;231(3):e13584. doi: 10.1111/apha.13584. Epub 2020 Dec 6. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 33222426
-
Organization of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina: electron microscopy of Golgi-impregnated cells.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 May 7;258(823):261-83. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0036. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970. PMID: 22408829
-
The neuronal organization of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina.Int Rev Cytol. 1984;86:285-320. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60181-3. Int Rev Cytol. 1984. PMID: 6368448 Review.
-
Bipolar Cell Pathways in the Vertebrate Retina.2007 May 24 [updated 2012 Jan 20]. In: Kolb H, Fernandez E, Jones B, Nelson R, editors. Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System [Internet]. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center; 1995–. 2007 May 24 [updated 2012 Jan 20]. In: Kolb H, Fernandez E, Jones B, Nelson R, editors. Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System [Internet]. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center; 1995–. PMID: 21413382 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
High temporal frequency light response in mouse retina requires FAT3 signaling in bipolar cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 28:2023.11.02.565326. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.02.565326. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Gen Physiol. 2025 Mar 03;157(2):e202413642. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202413642. PMID: 37961274 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
ERG responses to high-frequency flickers require FAT3 signaling in mouse retinal bipolar cells.J Gen Physiol. 2025 Mar 3;157(2):e202413642. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202413642. Epub 2025 Feb 4. J Gen Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39903280 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Retinal Synapse Development.Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024 Sep;10(1):377-402. doi: 10.1146/annurev-vision-102122-105721. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39292551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatial organization of the mouse retina at single cell resolution by MERFISH.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 15;14(1):4929. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40674-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37582959 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology and connectivity of retinal horizontal cells in two avian species.Front Cell Neurosci. 2025 Mar 4;19:1558605. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1558605. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40103750 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

