Discovery of Potent EGFR Inhibitors With 6-Arylureido-4-anilinoquinazoline Derivatives
- PMID: 34122069
- PMCID: PMC8187944
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647591
Discovery of Potent EGFR Inhibitors With 6-Arylureido-4-anilinoquinazoline Derivatives
Abstract
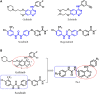
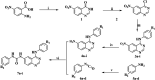
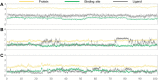
According to the classical pharmacophore fusion strategy, a series of 6-arylureido-4-anilinoquinazoline derivatives ( Compounds 7a - t ) were designed, synthesized, and biologically evaluated by the standard CCK-8 method and enzyme inhibition assay. Among the title compounds, Compounds 7a , 7c , 7d , 7f , 7i , 7o , 7p , and 7q exhibited promising anti-proliferative bioactivities, especially Compound 7i , which had excellent antitumor activity against the A549, HT-29, and MCF-7 cell lines (IC50 = 2.25, 1.72, and 2.81 μM, respectively) compared with gefitinib, erlotinib, and sorafenib. In addition, the enzyme activity inhibition assay indicated that the synthesized compounds had sub-micromolar inhibitory levels (IC50, 11.66-867.1 nM), which was consistent with the results of the tumor cell line growth inhibition tests. By comparing the binding mechanisms of Compound 7i (17.32 nM), gefitinib (25.42 nM), and erlotinib (33.25 nM) to the EGFR, it was found that Compound 7i could extend into the effective region with a similar action conformation to that of gefitinib and interact with residues L85, D86, and R127, increasing the binding affinity of Compound 7i to the EGFR. Based on the molecular hybridization strategy, 14 compounds with EGFR inhibitory activity were designed and synthesized, and the action mechanism was explored through computational approaches, providing valuable clues for the research of antitumor agents based on EGFR inhibitors.
Keywords: EGFR; anti-proliferative bioactivities; enzyme activity inhibition assay; molecular docking; molecular dynamic simulation.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Xue, Liu, Wang, Yan, Liu, Wang, Shi, Cao, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

