Advances in Screening, Early Diagnosis and Accurate Staging of Diabetic Neuropathy
- PMID: 34122344
- PMCID: PMC8188984
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.671257
Advances in Screening, Early Diagnosis and Accurate Staging of Diabetic Neuropathy
Abstract
The incidence of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes is increasing worldwide. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is among the most distressing and costly of all the chronic complications of diabetes and is a cause of significant disability and poor quality of life. This incurs a significant burden on health care costs and society, especially as these young people enter their peak working and earning capacity at the time when diabetes-related complications most often first occur. DPN is often asymptomatic during the early stages; however, once symptoms and overt deficits have developed, it cannot be reversed. Therefore, early diagnosis and timely intervention are essential to prevent the development and progression of diabetic neuropathy. The diagnosis of DPN, the determination of the global prevalence, and incidence rates of DPN remain challenging. The opinions vary about the effectiveness of the expansion of screenings to enable early diagnosis and treatment initiation before disease onset and progression. Although research has evolved over the years, DPN still represents an enormous burden for clinicians and health systems worldwide due to its difficult diagnosis, high costs related to treatment, and the multidisciplinary approach required for effective management. Therefore, there is an unmet need for reliable surrogate biomarkers to monitor the onset and progression of early neuropathic changes in DPN and facilitate drug discovery. In this review paper, the aim was to assess the currently available tests for DPN's sensitivity and performance.
Keywords: Diabetic Neuropathy; Diagnosis; Early Detection; Screening; microvascular complications; neuropathy biomarkers.
Copyright © 2021 Carmichael, Fadavi, Ishibashi, Shore and Tavakoli.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

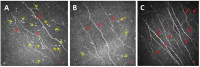
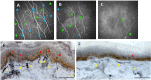
References
-
- Neeland IJ, Patel KV. Chapter 4 - Diabetes: Key Markers of Injury and Prognosis. In: Nambi V, editor. Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Disease. Netherlands: Elsevier; (2019). p. 41–51.
-
- Internation Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation; (2019). Available at: https://diabetesatlas.org/en/sections/worldwide-toll-of-diabetes.html.
-
- Diabetes UK . Us, diabetes and a lot of facts and stats. London, UK: Diabetes UK; (2019). Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/resources-s3/2019-02/1362B_Facts%20and%20sta....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

