An integrated console for capsule-based, automated organic synthesis
- PMID: 34123325
- PMCID: PMC8153237
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc01048d
An integrated console for capsule-based, automated organic synthesis
Abstract
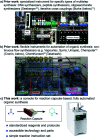
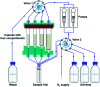
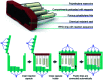
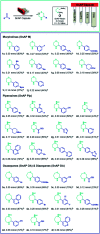
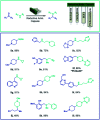
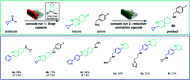
The current laboratory practices of organic synthesis are labor intensive, impose safety and environmental hazards, and hamper the implementation of artificial intelligence guided drug discovery. Using a combination of reagent design, hardware engineering, and a simple operating system we provide an instrument capable of executing complex organic reactions with prepacked capsules. The machine conducts coupling reactions and delivers the purified products with minimal user involvement. Two desirable reaction classes - the synthesis of saturated N-heterocycles and reductive amination - were implemented, along with multi-step sequences that provide drug-like organic molecules in a fully automated manner. We envision that this system will serve as a console for developers to provide synthetic methods as integrated, user-friendly packages for conducting organic synthesis in a safe and convenient fashion.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
This technology was developed with the support of funding from the Swiss Commission for Technology Innovation, the ETH Pioneer Fellowships, and the European Research Council and licensed to the ETH spinoff company Synple Chem AG. B. M. W., P. L. N., K.-Y. C. and J. W. B. are listed as inventors of a patent (WO Pat., WO2017121724A1, 2016) related to this technology. B. M. W., P. L. N., T. J. and J. W. B. are co-founders of Synple Chem AG.
Figures

References
-
- Mehr S. H. M. Craven M. Leonov A. I. Keenan G. Cronin L. Science. 2020;370:101. - PubMed
-
- IBM RXN for Chemistry, https://rxn.res.ibm.com, accessed Jan 05, 2021
-
- Coley C. W. Thomas D. A. Lummiss J. A. M. Jaworski J. N. Breen C. P. Schultz V. Hart T. Fishman J. S. Rogers L. Gao H. Hicklin R. W. Plehiers P. P. Byington J. Piotti J. S. Green W. H. Hart A. J. Jamison T. F. Jensen K. F. Science. 2019;365:eaax1566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

