Identification of potential gene signatures associated with osteosarcoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 34123594
- PMCID: PMC8164836
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11496
Identification of potential gene signatures associated with osteosarcoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most primary malignant bone cancer in children and adolescents with a high mortality rate. This work aims to screen novel potential gene signatures associated with OS by integrated microarray analysis of the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database.
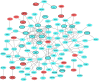
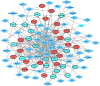
Material and methods: The OS microarray datasets were searched and downloaded from GEO database to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between OS and normal samples. Afterwards, the functional enrichment analysis, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis and transcription factor (TF)-target gene regulatory network were applied to uncover the biological function of DEGs. Finally, two published OS datasets (GSE39262 and GSE126209) were obtained from GEO database for evaluating the expression level and diagnostic values of key genes.
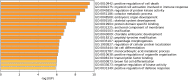
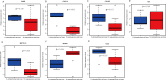
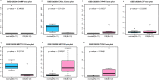
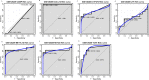
Results: In total 1,059 DEGs (569 up-regulated DEGs and 490 down-regulated DEGs) between OS and normal samples were screened. Functional analysis showed that these DEGs were markedly enriched in 214 GO terms and 54 KEGG pathways such as pathways in cancer. Five genes (CAMP, METTL7A, TCN1, LTF and CXCL12) acted as hub genes in PPI network. Besides, METTL7A, CYP4F3, TCN1, LTF and NETO2 were key genes in TF-gene network. Moreover, Pax-6 regulated four key genes (TCN1, CYP4F3, NETO2 and CXCL12). The expression levels of four genes (METTL7A, TCN1, CXCL12 and NETO2) in GSE39262 set were consistent with our integration analysis. The expression levels of two genes (CXCL12 and NETO2) in GSE126209 set were consistent with our integration analysis. ROC analysis of GSE39262 set revealed that CYP4F3, CXCL12, METTL7A, TCN1 and NETO2 had good diagnostic values for OS patients. ROC analysis of GSE126209 set revealed that CXCL12, METTL7A, TCN1 and NETO2 had good diagnostic values for OS patients.
Keywords: Activating transcription factor; Bioinformatic; Diagnosis; Genes; Osteosarcoma.
©2021 Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bielack SSK-BB, Delling G, Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M, Winkelmann W, Zoubek A, Jürgens H, Winkler K. Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremities or trunk: an analysis of 1, 702 patients treated on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2002;20:776–790. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.20.3.776. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coffelt SBMF, Watson K, Zwezdaryk KJ, Dembinski JL, LaMarca HL, Tomchuck SL, Honerzu Bentrup K, Danka ES, Henkle SL, Scandurro AB. The pro-inflammatory peptide LL-37 promotes ovarian tumor progression through recruitment of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2019;106:3806–3811. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

