Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
- PMID: 34123764
- PMCID: PMC8170385
- DOI: 10.5395/rde.2021.46.e28
Effect of number of uses and sterilization on the instrumented area and resistance of reciprocating instruments
Abstract
Objectives: This study evaluated the effect of repeated uses and autoclaving in the instrumented area, fracture resistance, and time of instrumentation of thermally treated nickel-titanium reciprocating systems.
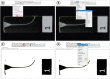
Materials and methods: Two hundred simulated canals were instrumented using Reciproc Blue and WaveOne Gold. Each file was used up to 10 times or until fracture. The instrumented area was measured in pre- and post-operative images, using ImageJ software. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis evaluated the number of uses of instruments before fracture. Instrumented area and time of instrumentation were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis. Correlations among the number of uses and instrumented area were measured. The level of statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
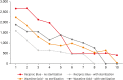
Results: Reciproc Blue presented a higher estimated number of uses in comparison with WaveOne Gold (p = 0.026), but autoclaving did not affect the resistance to fracture of instruments (p > 0.05). The instrumented area was different among the evaluated groups (p = 0.039), and the instrumented area along the uses of both tested instruments was reduced. With the time of instrumentation, there was also a significant difference among the evaluated groups; the groups without sterilization cycles were faster, in comparison to those submitted to autoclaving (p = 0.010).
Conclusions: Reciproc Blue was more resistant than WaveOne Gold, suffering later fracture. Additionally, the sterilization cycles did not influence the estimated number of uses of thermally treated reciprocating instruments, but the instrumented area of root canals was reduced along with the repeated uses of both instruments.
Keywords: Instrument fracture; Instrumentation; Reciproc Blue; Sterilization; WaveOne Gold.
Copyright © 2021. The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Hasheminia SM, Farhad A, Sheikhi M, Soltani P, Hendi SS, Ahmadi M. Cone-beam computed tomographic analysis of canal transportation and centering ability of single-file systems. J Endod. 2018;44:1788–1791. - PubMed
-
- Es-Souni M, Es-Souni M, Brandies HF. On the transformation behaviour, mechanical properties and biocompatibility of two NiTi-based shape memory alloys: NiTi42 and NiTi42Cu7. Biomaterials. 2001;22:2153–2161. - PubMed
-
- Zupanc J, Vahdat-Pajouh N, Schäfer E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys - a review. Int Endod J. 2018;51:1088–1103. - PubMed
-
- Kiefner P, Ban M, De-Deus G. Is the reciprocating movement per se able to improve the cyclic fatigue resistance of instruments? Int Endod J. 2014;47:430–436. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

