RT-qPCR Assays for Rapid Detection of the N501Y, 69-70del, K417N, and E484K SARS-CoV-2 Mutations: A Screening Strategy to Identify Variants With Clinical Impact
- PMID: 34123874
- PMCID: PMC8195289
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.672562
RT-qPCR Assays for Rapid Detection of the N501Y, 69-70del, K417N, and E484K SARS-CoV-2 Mutations: A Screening Strategy to Identify Variants With Clinical Impact
Abstract
Background: Several variants of the SARS-CoV-2 have been documented globally during the current COVID-19 pandemic. The N501Y, 69-70del, K417N, and E484K SARS-CoV-2 mutations have been documented among the most relevant due to their potential pathogenic biological effects. This study aimed to design, validate, and propose a fast real-time RT-qPCR assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 mutations with possible clinical and epidemiological relevance in the Mexican population.
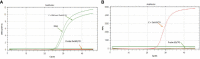
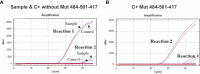
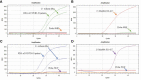
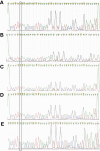
Methods: Targeting spike (S) gene mutations of SARS-CoV-2 (N501Y, 69-70del, K417N, and E484K), specific primers, and probes for three specific quantitative reverse transcription PCR (RT-qPCR) assays were designed, and validated using Sanger sequencing. These assays were applied in clinical samples of 1060 COVID-19 patients from Jalisco Mexico.
Results: In silico analyzes showed high specificity of the three assays. Amplicons of samples were confirmed through sequencing. The screening of samples of COVID-19 patients allowed the identification of the E484K mutation in nine individuals and the identification of P.2 Brazilian variant in Mexico.
Conclusion: This work provides low-cost RT-qPCR assays for rapid screening and molecular surveillance of mutations with potential clinical impact. This strategy allowed the detection of E484K mutation and P.2 variant for the first time in samples from the Mexican population.
Keywords: E484K; P.2 variant detection; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2 mutation screening; SARS-CoV-2 mutations; epidemiological surveillance; molecular screening.
Copyright © 2021 Vega-Magaña, Sánchez-Sánchez, Hernández-Bello, Venancio-Landeros, Peña-Rodríguez, Vega-Zepeda, Galindo-Ornelas, Díaz-Sánchez, García-Chagollán, Macedo-Ojeda, García-González and Muñoz-Valle.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors RS-S, AV-L, RV-Z, BG-O, MD-S, and OG-G have a working relationship with Genes2Life SAPI de CV. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bal A., Destras G., Gaymard A., Stefic K., Marlet J., Eymieux S., et al. . (2021). Two-Step Strategy for the Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern 202012/01 and Other Variants With Spike Deletion H69-V70, France, August to December 2020. Euro Surveill. 26. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.9.210013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolotin S., Robertson A. V., Eshaghi A., De Lima C., Lombos E., Chong-King E., et al. . (2009). Development of a Novel Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase PCR Method for the Detection of H275Y Positive Influenza A H1N1 Isolates. J. Virol. Methods 158, 190–194. 10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.01.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

