Effect of COVID-19 on control of T1DM patients in Aseer region of Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 34123921
- PMCID: PMC8144754
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2333_20
Effect of COVID-19 on control of T1DM patients in Aseer region of Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background: The novel corona virus disease, also known as COVID-19, has emerged as a major health concern globally. Its association with comorbid condition has increased its mortality. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with increased risk of infection in comparison to general population. This risk is higher in type 1 DM that type 2 DM.
Methods: A cross sectional study was done in T1DM patients in whom a structured questionnaire was administered after lockdown. Data regarding social demographical variables, Information regarding sugar levels, psychological effects, changes in weight, exercise habits and other variables were included in the validated, electronic questionnaire. Ethic approval was obtained from the Diabetic center Abha, study duration was from January-2020 to October-2020.
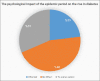
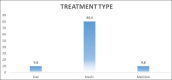
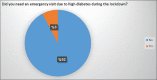
Results: Out of 143 total patients (46.9%) were males while 53.1% were females. Mean ± S.D of age was obtained 29.6 ± 1.8. [Figure 1] depicted that 23% of the respondents were effected psychologically. [Figure 2] depicted that 80.4% used insulin as a treatment. [Figure 3] depicted that 8% of the respondents make an emergency visit to the health care centers for high rise in diabetes during lockdown.
Conclusion: COVID-19 and the lockdown affected the management of T1DM. It resulted in changes in lifestyle, compliance to medication, and psychological impact on the participant.
Keywords: Covid-19; diabetes; lockdown; psychology; type 1.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 Lockdown and Lifestyle Changes in Saudi Adults With Types 1 and 2 Diabetes.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 8;10:912816. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.912816. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35875025 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge of Diabetes Mellitus and Practices Regarding Lifestyle Factors and Diabetes Management in a General Adult Population of Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Jul 23;17:2775-2787. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S461807. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39077554 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of hypoglycemia and its risk factors among diabetics during Ramadan in Abha city, Aseer Region, KSA.J Family Med Prim Care. 2019 Sep 30;8(9):2793-2798. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_250_19. eCollection 2019 Sep. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019. PMID: 31681644 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of COVID-19 on Patients with Diabetes Standard of Care in the Jazan Region, Saudi Arabia.Mater Sociomed. 2022 Dec;34(4):272-277. doi: 10.5455/msm.2022.34.272-277. Mater Sociomed. 2022. PMID: 36936887 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on diabetes patients in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020 Sep-Oct;14(5):1583-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.051. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 32947759 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 Lockdown and Lifestyle Changes in Saudi Adults With Types 1 and 2 Diabetes.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 8;10:912816. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.912816. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35875025 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic in people with type 1 diabetes: A systematic literature review.J Psychosom Res. 2023 May;168:111206. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2023.111206. Epub 2023 Feb 28. J Psychosom Res. 2023. PMID: 36913765 Free PMC article.
-
The Experiences of People with Diabetes during COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 29;19(1):340. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19010340. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 35010603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guan W-J, Ni Z-Y, Hu Y, Liang W-H, Ou C-Q, He J-X, et al. For the China medical treatment expert group for Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1708–20. - PubMed
-
- Maddaloni E, Coraggio L, Pieralice S, Carlone A, Pozzilli P, Buzzetti R. Effects of COVID-19 lockdown on glucose control: Continuous glucose monitoring data from people with diabetes on intensive insulin therapy. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:e86–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources