Health Related Social Needs Among Chinese American Primary Care Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications for Cancer Screening and Primary Care
- PMID: 34123992
- PMCID: PMC8192797
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.674035
Health Related Social Needs Among Chinese American Primary Care Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Implications for Cancer Screening and Primary Care
Abstract
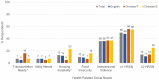
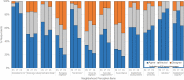
Research Objective: Initiatives to address social determinants of health (SDOH) and measure health-related social needs (HRSN) within clinic settings are increasing. However, few have focused on the specific needs of Asian Americans (AA). We examine the prevalence of HRSN during a period spanning the COVID-19 pandemic to inform strategies to improve cancer screening and primary care among AA patients. Methods: We implemented a self-administered HRSN screening tool in English and Chinese, traditional (T) or simplified (S) text, within a hospital-affiliated, outpatient primary care practice predominantly serving AA in New Jersey. HRSN items included food insecurity, transportation barriers, utility needs, interpersonal violence, housing instability, immigration history, and neighborhood perceptions on cohesion and trust. We conducted medical chart reviews for a subset of participants to explore the relationship between HRSN and history of cancer screening. Results: Among 236 participants, most were Asian (74%), non-US born (79%), and privately insured (57%). One-third responded in Chinese (37%). Half reported having ≥1 HRSN. Interpersonal violence was high across all participants. Transportation needs were highest among Chinese-T participants, while food insecurity and housing instability were higher among Chinese-S participants. Lower-income patients had higher odds of having ≥2 HRSN (OR:2.53, 95% CI: 1.12, 5.98). Older age and public insurance/uninsured were significantly associated with low neighborhood perceptions. Conclusions: We observed higher than anticipated reports of HRSN among primary care patients in a suburban, hospital-affiliated practice serving AA. Low neighborhood perceptions, particularly among Chinese-S participants, highlight the importance of addressing broader SDOH among insured, suburban AA patients. These study findings inform the need to augment HRSN identification to adequately address social needs that impact health outcomes and life course experiences for Asian patients. As HRSN measuring efforts continue, and COVID-19's impact on the health of minority communities emerge, it will be critical to develop community-specific referral pathways to connect AA to resources for HRSN and continue to address more upstream social determinants of health for those who are disproportionately impacted.
Keywords: Asian American (AA); COVID-19; cancer screening; primary care; social determinants; social needs.
Copyright © 2021 Tsui, Yang, Anuforo, Chou, Brogden, Xu, Cantor and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- CSDH . Closing the Gap in a Generation: Health Equity Through Action on the Social Determinants of Health. Final Report of the Commission on Social Determinants of Health. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2008). - PubMed
-
- Clegg LX, Reichman ME, Miller BA, Hankey BF, Singh GK, Lin YD, et al. Impact of socioeconomic status on cancer incidence and stage at diagnosis: selected findings from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results: national longitudinal mortality study. Cancer Causes Control. (2009) 20:417–35. 10.1007/s10552-008-9256-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine . Delivering high-quality cancer care: charting a new course for a system in crisis. In Levit LA, Balogh EP, Nass SJ, Ganz PA. editors. Delivering High Quality Cancer Care. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press; (2013). p. 412. - PubMed
-
- Polite BN, Adams-Campbell LL, Brawley OW, Bickell N, Carethers JM, Flowers CR, et al. Charting the future of cancer health disparities research: a position statement from the american association for cancer research, the american cancer society, the american society of clinical oncology, and the national cancer institute. J Clin Oncol. (2017) 35:3075–82. 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.6546 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials