Computational Analysis and Phylogenetic Clustering of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes
- PMID: 34124300
- PMCID: PMC8160537
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3999
Computational Analysis and Phylogenetic Clustering of SARS-CoV-2 Genomes
Abstract
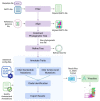
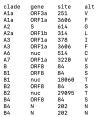
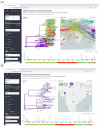
COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, originated as an isolated outbreak in the Hubei province of China but soon created a global pandemic and is now a major threat to healthcare systems worldwide. Following the rapid human-to-human transmission of the infection, institutes around the world have made efforts to generate genome sequence data for the virus. With thousands of genome sequences for SARS-CoV-2 now available in the public domain, it is possible to analyze the sequences and gain a deeper understanding of the disease, its origin, and its epidemiology. Phylogenetic analysis is a potentially powerful tool for tracking the transmission pattern of the virus with a view to aiding identification of potential interventions. Toward this goal, we have created a comprehensive protocol for the analysis and phylogenetic clustering of SARS-CoV-2 genomes using Nextstrain, a powerful open-source tool for the real-time interactive visualization of genome sequencing data. Approaches to focus the phylogenetic clustering analysis on a particular region of interest are detailed in this protocol.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Genomes; Phylogenetic analysis; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures



References
-
- Babakir-Mina M., Ciccozzi M., Ciotti M., Marcuccilli F., Balestra E., Dimonte S., Perno C. F. and Aquaro S.(2009). Phylogenetic analysis of the surface proteins of influenza A(H5N1) viruses isolated in Asian and African populations. New Microbiol 32(4): 397-403. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

