Prognostic value of inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19 in Indonesia
- PMID: 34124411
- PMCID: PMC8186126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100803
Prognostic value of inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19 in Indonesia
Abstract
Background & aims: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has a wide clinical spectrum, ranging from asymptomatic infection to severe diseases with high mortality rate. Early identification of high-risk COVID-19 patients may be beneficial to reduce morbidity and in-hospital mortality. This study aimed to investigate whether baseline levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and immune-cell-based inflammatory indices, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), derived-NLR (d-NLR), and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) at hospital admission are associated with adverse disease outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
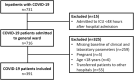
Methods: Clinical data from 391 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in three Siloam Hospitals in Indonesia were retrospectively collected and analysed from March 20 to October 30, 2020.
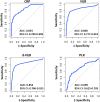
Results: Fifty-four (13.8%) hospitalized patients had clinical deterioration and required ICU treatment, categorizing them as severe COVID-19 cases. Older age, presence of underlying diseases, and increased inflammatory markers values at admission were significantly associated with severe cases. After adjustment of sociodemographic and comorbidities factors, CRP, NLR, and d-NLR values, but not PLRs, were identified as independent risk factors for disease severity and death in COVID-19 patients. The area under curve (AUC) of CRP, NLR, and d-NLR were 0.854, 0.848, and 0.854, respectively. The optimal cut-off points for CRP, NLR, and d-NLR for identification of COVID-19 patients with potential worse disease outcomes were 47 mg/L, 6, and 4, respectively.
Conclusion: Initial assessment of CRP, NLR, and d-NLR values at hospital admission may be important predictors for adverse disease outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; COVID-19; Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; Risk factors.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Update on Coronavirus Disease in Indonesia. World Health Organization; 2021. https://www.who.int/indonesia/news/novel-coronavirus
-
- Situasi terkini perkembangan coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia 2021. https://infeksiemerging.kemkes.go.id/situasi-infeksi-emerging/situasi-te... Feburary 28, 2021.
-
- Wu Z., McGoogan J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. J Am Med Assoc. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. - PubMed
-
- Phua J., Faruq M.O., Kulkarni A.P., et al. Critical care bed capacity in Asian countries and regions. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(5):654–662. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
