Titanium Dioxide/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cork Nanocomposite: A Floating Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Methylene Blue under Irradiation of a Visible Light Source
- PMID: 34124472
- PMCID: PMC8190905
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01458
Titanium Dioxide/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Cork Nanocomposite: A Floating Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Methylene Blue under Irradiation of a Visible Light Source
Abstract
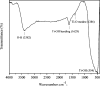
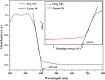
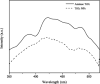
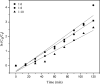
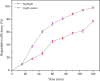
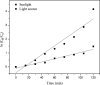
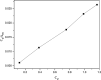
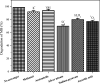
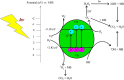
Photocatalytic degradation by the titanium dioxide (TiO2) photocatalyst attracts tremendous interest due to its promising strategy to eliminate pollutants from wastewater. The floating photocatalysts are explored as potential candidates for practical wastewater treatment applications that could overcome the drawbacks posed by the suspended TiO2 photocatalysis system. The problem occurs when the powdered TiO2 applied directly into the treated solution will form a slurry, making its reuse become a difficult step after treatment. In this study, the immobilization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) on the floating substrate (cork) employing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as a binder to anchor TiO2 NPs on the surface of the cork was carried out. Characterizations such as Fourier transformer infrared, X-ray diffraction (XRD), ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-vis), zeta potential, photoluminescence spectroscopy, femtosecond to millisecond time-resolved visible to mid-IR absorption spectroscopy, ion chromatography, and scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) analyses were employed. XRD analysis revealed the formation of anatase-phase TiO2 NPs. The results demonstrated that the crystallite size was 9.36 nm. The band gap energy of TiO2 NPs was determined as 3.0 eV. PL analysis verified that TiO2 NPs possessed a slower recombination rate of electron-hole pairs as compared to anatase TiO2. The result was attributed by the behavior of photogenerated charge carriers on TiO2 NPs, which existed as shallowly trapped electrons that could survive longer than a few milliseconds in this study. Furthermore, SEM-EDX analysis indicated that TiO2 NPs were well distributed on the surface of the cork. At the optimal mole ratio of TiO2/PVA (1:8), the TiO2/PVA/cork floating photocatalyst degraded at 98.43% of methylene blue (MB) under a visible light source which performed better than under sunlight irradiation (77.09% of MB removal) for 120 min. Besides, the mineralization result has measured the presence of sulfate anions after photocatalytic activities, which achieved 86.13% (under a visible light source) and 65.34% (under sunlight). The superior photodegradation performance for MB was mainly controlled by the reactive oxygen species of the superoxide radical (•O2 -). The degradation kinetics of MB followed the first-order kinetics. Meanwhile, the Langmuir isotherm model was fitted for the adsorption isotherm. The floating photocatalyst presented good reusability, resulting in 78.13% of MB removal efficiency even after five cycles. Our TiO2/PVA/cork floating photocatalyst fabrication and high photocatalytic performance are potentially used in wastewater treatment, especially under visible light irradiation.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
One-step co-precipitation synthesis, characterization, and enhanced photocatalytic performance of CaO/TiO2-supported γ-Al2O3 nanocomposites (NCs) in wastewater treatment.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 15;15(30):24851-24861. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03493k. eCollection 2025 Jul 10. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40666418 Free PMC article.
-
One dimensional CdS nanowire@TiO2 nanoparticles core-shell as high performance photocatalyst for fast degradation of dye pollutants under visible and sunlight irradiation.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016 Oct 1;479:43-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.036. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2016. PMID: 27348482
-
Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles from Bacillus subtilis MTCC 8322 and its application for the removal of methylene blue and orange G dyes under UV light and visible light.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 8;11:1323249. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1323249. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38260746 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in photocatalytic degradation of industrial organic dye by utilising the silver doped titanium dioxide nanocomposite.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 5;10(24):e40998. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40998. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39720083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of TiO2/PPy nanocomposite for photocatalytic applications; synthesis, characterization, and combination with various substrates: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jun;31(30):42521-42546. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-33893-8. Epub 2024 Jun 15. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38878243 Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic Fabrication of Monodisperse and Recyclable TiO2-Poly(ethylene glycol) Diacrylate Hybrid Microgels for Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Medium.Langmuir. 2023 Dec 26;39(51):18784-18796. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c02276. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Langmuir. 2023. PMID: 38093553 Free PMC article.
-
The enhanced photocatalytic performance and first-principles computational insights of Ba doping-dependent TiO2 quantum dots.Nanoscale Adv. 2022 Aug 16;4(18):3996-4008. doi: 10.1039/d2na00361a. eCollection 2022 Sep 13. Nanoscale Adv. 2022. PMID: 36133333 Free PMC article.
-
Facile Sol-Gel Synthesis of C, N Codoped-TiO2 for Efficient Degradation of Palm Oil Mill Effluent.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 11;10(3):2858-2870. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08813. eCollection 2025 Jan 28. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39895745 Free PMC article.
-
Novel and Reusable Graphene Oxide-Coated Reticulated Open-Cell Mullite Foams for Methylene Blue Dye Adsorption.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 24;9(5):5541-5547. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07569. eCollection 2024 Feb 6. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38343932 Free PMC article.
-
Ag₃PO₄@ZnO kraft lignin composite for optimized photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using response surface methodology.Sci Rep. 2025 Jun 20;15(1):20165. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05597-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40542064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subki N. S.Environmental contamination by batik wastewater and the potential application of activated carbon from pineapple waste for wastewater treatment. Ph. D. Thesis, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia, 2017.
-
- Zhang X.; Yin Y.; Sun Z.; Du Y.; Ma S.; Wu Y. Cr/S/TiO2-loaded hollow glass microspheres as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for the photocatalytic degradation of indigo carmine under visible light. Quim. Nova 2016, 39, 956–961.
-
- Gao Y.; Wang T. Preparation of Ag2O/TiO2 nanocomposites by two-step method and study of its degradation of RhB. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129049.10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.129049. - DOI
-
- Li W.; Zuo Y.; Jiang L.; Yao D.; Chen Z.; He G.; Chen H. Bi2Ti2O7/TiO2/RGO composite for the simulated sunlight-driven photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 256, 123650.10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123650. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

