Key Metabolic Enzymes Involved in Remdesivir Activation in Human Lung Cells
- PMID: 34125594
- PMCID: PMC8370248
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00602-21
Key Metabolic Enzymes Involved in Remdesivir Activation in Human Lung Cells
Abstract
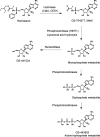
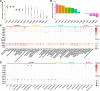
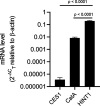
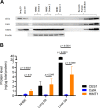
Remdesivir (RDV; GS-5734, Veklury), the first FDA-approved antiviral to treat COVID-19, is a single-diastereomer monophosphoramidate prodrug of an adenosine analogue. RDV is taken up in the target cells and metabolized in multiple steps to form the active nucleoside triphosphate (TP) (GS-443902), which, in turn, acts as a potent and selective inhibitor of multiple viral RNA polymerases. In this report, we profiled the key enzymes involved in the RDV metabolic pathway with multiple parallel approaches: (i) bioinformatic analysis of nucleoside/nucleotide metabolic enzyme mRNA expression using public human tissue and lung single-cell bulk mRNA sequence (RNA-seq) data sets, (ii) protein and mRNA quantification of enzymes in human lung tissue and primary lung cells, (iii) biochemical studies on the catalytic rate of key enzymes, (iv) effects of specific enzyme inhibitors on the GS-443902 formation, and (v) the effects of these inhibitors on RDV antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture. Our data collectively demonstrated that carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) and cathepsin A (CatA) are enzymes involved in hydrolyzing RDV to its alanine intermediate MetX, which is further hydrolyzed to the monophosphate form by histidine triad nucleotide-binding protein 1 (HINT1). The monophosphate is then consecutively phosphorylated to diphosphate and triphosphate by cellular phosphotransferases. Our data support the hypothesis that the unique properties of RDV prodrug not only allow lung-specific accumulation critical for the treatment of respiratory viral infection such as COVID-19 but also enable efficient intracellular metabolism of RDV and its MetX to monophosphate and successive phosphorylation to form the active TP in disease-relevant cells.
Keywords: CES1; COVID-19; CatA; HINT1; SARS-CoV-2; nucleotide analogs; prodrug activation; remdesivir.
Figures


References
-
- Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Graham RL, Menachery VD, Gralinski LE, Case JB, Leist SR, Pyrc K, Feng JY, Trantcheva I, Bannister R, Park Y, Babusis D, Clarke MO, Mackman RL, Spahn JE, Palmiotti CA, Siegel D, Ray AS, Cihlar T, Jordan R, Denison MR, Baric RS. 2017. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci Transl Med 9:eaal3653. 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3653. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Leist SR, Schafer A, Won J, Brown AJ, Montgomery SA, Hogg A, Babusis D, Clarke MO, Spahn JE, Bauer L, Sellers S, Porter D, Feng JY, Cihlar T, Jordan R, Denison MR, Baric RS. 2020. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat Commun 11:222. 10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birkus G, Wang R, Liu XH, Kutty N, MacArthur H, Cihlar T, Gibbs C, Swaminathan S, Lee W, McDermott M. 2007. Cathepsin A is the major hydrolase catalyzing the intracellular hydrolysis of the antiretroviral nucleotide phosphonoamidate prodrugs GS-7340 and GS-9131. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:543–550. 10.1128/AAC.00968-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

