Establishment of time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay of IgG4 based on magnetic microspheres
- PMID: 34125973
- PMCID: PMC8373317
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23874
Establishment of time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay of IgG4 based on magnetic microspheres
Abstract
Background: The abnormal increase in serum IgG4 level is an important clinical symptom of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), and the detection of serum IgG4 level is a powerful tool for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. This study was conducted to establish a simple and rapid immunoassay for the determination of human serum IgG4 levels.
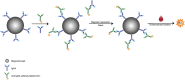
Methods: Based on the competition method, a novel immunoassay was established for the determination of human serum IgG4 using a combination of time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay (TRFIA) and magnetic microspheres. IgG4 was coupled with magnetic microspheres and competed with IgG4 in the samples to bind the Eu3+ -labeled anti-IgG4 antibody. The immunocomplex was separated and washed in a magnetic field, and the fluorescence counts were measured according to the number of dissociated europium ions.
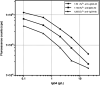
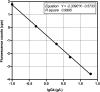
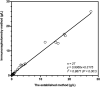
Results: The analytical sensitivity of IgG4-TRFIA based on magnetic microspheres was 0.006 g/L, and the detection range was 0.006-20 g/L under optimal conditions. The precision, recovery, and specificity of this immunoassay were demonstrated to be acceptable. The clinical application of IgG4-TRFIA based on magnetic microspheres was evaluated and compared with that of immunonephelometry. The results showed that the two detection methods had a good correlation, with a correlation coefficient of .9871.
Conclusion: IgG4-TRFIA based on magnetic microspheres has the advantages of high sensitivity, wide detection range, and short analysis time and has the potential to become a useful tool for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD.
Keywords: IgG4; IgG4-RD; immunoassay; magnetic microspheres; time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(10):732‐738. - PubMed
-
- Himi T, Takano K, Yamamoto M, Naishiro Y, Takahashi H. A novel concept of Mikulicz's disease as IgG4‐related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012;39(1):9‐17. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Stone PH. Management of IgG4‐related disease. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019;1(1):e55‐e65. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4‐related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(10):982‐984. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

