A dynamic nomogram for predicting the risk of asthma: Development and validation in a database study
- PMID: 34125979
- PMCID: PMC8275008
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23820
A dynamic nomogram for predicting the risk of asthma: Development and validation in a database study
Abstract
Background: Asthma remains a serious health problem with increasing prevalence and incidence. This study was to develop and validate a dynamic nomogram for predicting asthma risk.
Methods: Totally 597 subjects whose age ≥18 years old with asthma, an accurate age at first cigarette, and clear smoking status were selected from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database (2013-2018). The dataset was randomly split into the training set and the testing set at a ratio of 4:6. Simple and multiple logistic regressions were used for identifying independent predictors. Then the nomogram was developed and internally validated using data from the testing set. The receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve was used for assessing the performance of the nomogram.
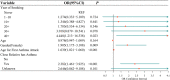
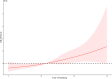
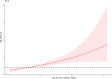
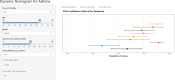
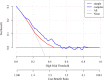
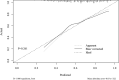
Results: According to the simple and multiple logistic regressions, smoking ≥40 years, female gender, the age for the first smoking, having close relative with asthma were independently associated with the risk of an asthma attack. The nomogram was thereby developed with the link of https://yanglifen.shinyapps.io/Dynamic_Nomogram_for_Asthma/. The ROC analyses showed an AUC of 0.726 (0.724-0.728) with a sensitivity of 0.887 (0.847-0.928) in the training set, and an AUC of 0.702 (0.700-0.703) with a sensitivity of 0.860 (0.804-0.916) in the testing set, fitting well in calibration curves. Decision curve analysis further confirmed the clinical usefulness of the nomogram.
Conclusion: Our dynamic nomogram could help clinicians to assess the individual probability of asthma attack, which was helpful for improving the treatment and prognosis of asthma.
Keywords: NHANES database; asthma; dynamic nomogram; smoking duration.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Risk factor analysis and nomogram for predicting poor symptom control in smoking asthmatics.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jun 1;24(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03076-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38824531 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting depression risk in patients with chronic kidney disease based on NHANES 2005-2018.J Health Popul Nutr. 2025 Apr 25;44(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00890-7. J Health Popul Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40281636 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic online nomogram for predicting depression risk in cancer patients based on NHANES 2007-2018.J Affect Disord. 2025 Sep 15;385:119402. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2025.119402. Epub 2025 May 13. J Affect Disord. 2025. PMID: 40374093
-
Development and validation of a depression risk prediction nomogram for US Adults with hypertension, based on NHANES 2007-2018.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 5;18(4):e0284113. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284113. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37018322 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for prediction of distant metastasis in children with wilms tumor: A study based on SEER database.J Pediatr Urol. 2020 Aug;16(4):473.e1-473.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2020.05.158. Epub 2020 May 29. J Pediatr Urol. 2020. PMID: 32600949 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting cough variant asthma diagnosis.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jan 20;25(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03478-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39828728 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment, Prediction, and Validation of a Nomogram for Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients With Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Aug 19;2024:5583707. doi: 10.1155/2024/5583707. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39188897 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of dynamic nomogram and risk score models for T2DM: a retrospective cohort study in Beijing.BMC Public Health. 2022 Dec 9;22(1):2306. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14782-6. BMC Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36494707 Free PMC article.
-
A Web-Based Dynamic Nomogram to Predict the Risk of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcal Infection in Patients with Pneumonia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 16;14(6):633. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14060633. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38535053 Free PMC article.
-
Risk prediction model of cognitive performance in older people with cardiovascular diseases: a study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database.Front Public Health. 2025 Jan 13;12:1447366. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1447366. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39872098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collaborators GBDCRD . Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability‐adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5(9):691‐706. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Croisant S. Epidemiology of asthma. Prevalence and burden of disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;795:17‐29. - PubMed
-
- National Asthma Education and Prevention Program TEPotDaMoA . Expert Panel Report 3: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma. Bethesda, MD: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (US); 2007.

