Cowpea mosaic virus stimulates antitumor immunity through recognition by multiple MYD88-dependent toll-like receptors
- PMID: 34126409
- PMCID: PMC8542346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120914
Cowpea mosaic virus stimulates antitumor immunity through recognition by multiple MYD88-dependent toll-like receptors
Abstract
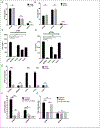
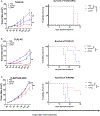
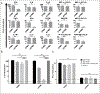
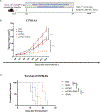
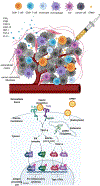
Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), a non-enveloped plant virus, and empty CPMV (eCPMV), a virus-like particle (VLP) composed of CPMV capsid without nucleic acids, are potent in situ cancer vaccines when administered intratumorally (I.T.). However, it is unclear how immune cells recognize these nanoparticles and why they are immunogenic, which was investigated in this study. CPMV generated stronger selective induction of cytokines and chemokines in naïve mouse splenocytes and exhibited more potent anti-tumor efficacy than eCPMV. MyD88 is required for both CPMV- and eCPMV-elicited immune responses. Screening with human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cell toll-like receptor (TLR) reporter assays along with experiments in corresponding TLR-/- mice indicated CPMV and eCPMV capsids are recognized by MyD88-dependent TLR2 and TLR4. CPMV, but not eCPMV, is additionally recognized by TLR7. Secretion of type I interferons (IFNs), which requires the interaction between TLR7 and encapsulated single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs), is critical to CPMV's better efficacy. The same recognition mechanisms are also functional in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Overall, these findings link CPMV immunotherapy efficacy with molecular recognition, provide rationale for how to develop more potent viral particles, accentuate the value of multi-TLR agonists as in situ cancer vaccines, and highlight the functional importance of type I IFNs for in situ vaccination.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Cowpea mosaic virus; In situ vaccination; Nanoparticle; Toll-like receptors; Virus-like nanoparticle.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing Interest:
Drs. Fiering and Steinmetz are co-founders of and have a financial relationship with Mosaic Immunoengineering Inc, which may be considered potential competing interest. The other authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lu J, Lee-Gabel L, Nadeau MC, Ferencz TM, & Soefje SA (2015). Clinical evaluation of compounds targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathway for cancer immunotherapy. Journal of oncology pharmacy practice : official publication of the International Society of Oncology Pharmacy Practitioners, 21(6), 451–467. 10.1177/1078155214538087 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yun S, Vincelette ND, Green MR, Wahner Hendrickson AE, & Abraham I. (2016). Targeting immune checkpoints in unresectable metastatic cutaneous melanoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 agents trials. Cancer medicine, 5(7), 1481–1491. 10.1002/cam4.732 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

