Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism: a link between the gut and brain for depression in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 34127024
- PMCID: PMC8204445
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02175-2
Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolism: a link between the gut and brain for depression in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
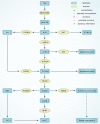
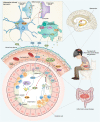
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which mainly includes ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease (CD), is a group of chronic bowel diseases that are characterized by abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bloody stools. IBD is strongly associated with depression, and its patients have a higher incidence of depression than the general population. Depression also adversely affects the quality of life and disease prognosis of patients with IBD. The tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway degrades more than 90% of tryptophan (TRP) throughout the body, with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), the key metabolic enzyme, being activated in the inflammatory environment. A series of metabolites of the pathway are neurologically active, among which kynerunic acid (KYNA) and quinolinic acid (QUIN) are molecules of great interest in recent studies on the mechanisms of inflammation-induced depression. In this review, the relationship between depression in IBD and the tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway is overviewed in the light of recent publications.
Keywords: Depression; IDO; Inflammatory bowel disease; The brain-gut axis; Tryptophan-kynurenine metabolic pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ng SC, Leung WK, Shi HY, Li MKK, Leung CM, Ng CKM, Lo FH, Hui YT, Tsang SWC, Chan YK, Loo CK, Chan KH, Hui AJ, Chow WH, Harbord M, Ching JYL, Lee M, Chan V, Tang W, Hung IFN, Ho J, Lao WC, Wong MTL, Sze SF, Shan EHS, Lam BCY, Tong RWH, Mak LY, Wong SH, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease from 1981 to 2014: results from a territory-wide population-based registry in Hong Kong. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016;22(8):1954–1960. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000846. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

