Kim-1 Targeted Extracellular Vesicles: A New Therapeutic Platform for RNAi to Treat AKI
- PMID: 34127536
- PMCID: PMC8722800
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020111561
Kim-1 Targeted Extracellular Vesicles: A New Therapeutic Platform for RNAi to Treat AKI
Abstract
Background: AKI is a significant public health problem with high morbidity and mortality. Unfortunately, no definitive treatment is available for AKI. RNA interference (RNAi) provides a new and potent method for gene therapy to tackle this issue.
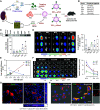
Methods: We engineered red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicles (REVs) with targeting peptides and therapeutic siRNAs to treat experimental AKI in a mouse model after renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Phage display identified peptides that bind to the kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1). RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) characterized the transcriptome of ischemic kidney to explore potential therapeutic targets.
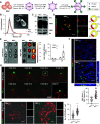
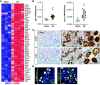
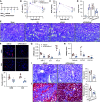
Results: REVs targeted with Kim-1-binding LTH peptide (REVLTH) efficiently homed to and accumulated at the injured tubules in kidney after I/R injury. We identified transcription factors P65 and Snai1 that drive inflammation and fibrosis as potential therapeutic targets. Taking advantage of the established REVLTH, siRNAs targeting P65 and Snai1 were efficiently delivered to ischemic kidney and consequently blocked the expression of P-p65 and Snai1 in tubules. Moreover, dual suppression of P65 and Snai1 significantly improved I/R- and UUO-induced kidney injury by alleviating tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis, and potently abrogated the transition to CKD.
Conclusions: A red blood cell-derived extracellular vesicle platform targeted Kim-1 in acutely injured mouse kidney and delivered siRNAs for transcription factors P65 and Snai1, alleviating inflammation and fibrosis in the tubules.
Keywords: P65; RNAi; Snai1; acute kidney injury; extracellular vesicles; kidney injury molecule-1.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA: Acute kidney injury. Lancet 394: 1949–1964, 2019 - PubMed
-
- See EJ, Jayasinghe K, Glassford N, Bailey M, Johnson DW, Polkinghorne KR, et al. .: Long-term risk of adverse outcomes after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies using consensus definitions of exposure. Kidney Int 95: 160–172, 2019 - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Xing G, Wang L, Wu Y, Li S, Xu G, et al. .; ISN AKF 0by25 China Consortiums : Acute kidney injury in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet 386: 1465–1471, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Setten RL, Rossi JJ, Han SP: The current state and future directions of RNAi-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 18: 421–446, 2019 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

