Genetic architecture of 11 organ traits derived from abdominal MRI using deep learning
- PMID: 34128465
- PMCID: PMC8205492
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.65554
Genetic architecture of 11 organ traits derived from abdominal MRI using deep learning
Abstract
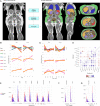
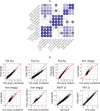
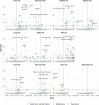
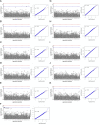
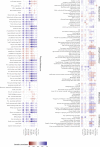
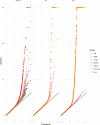
Cardiometabolic diseases are an increasing global health burden. While socioeconomic, environmental, behavioural, and genetic risk factors have been identified, a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms is required to develop more effective interventions. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been used to assess organ health, but biobank-scale studies are still in their infancy. Using over 38,000 abdominal MRI scans in the UK Biobank, we used deep learning to quantify volume, fat, and iron in seven organs and tissues, and demonstrate that imaging-derived phenotypes reflect health status. We show that these traits have a substantial heritable component (8-44%) and identify 93 independent genome-wide significant associations, including four associations with liver traits that have not previously been reported. Our work demonstrates the tractability of deep learning to systematically quantify health parameters from high-throughput MRI across a range of organs and tissues, and use the largest-ever study of its kind to generate new insights into the genetic architecture of these traits.
Keywords: adiposity; genetics; genome-wide association study; genomics; human; magnetic resonance imaging; medicine.
© 2021, Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YL, Nv, MC Employee, Calico Life Sciences LLC. This work was funded by Calico Life Sciences LLC. NB, BW, JB, ET No competing interests declared, ES Employee, Calico Life Sciences LLC.This work was funded by Calico Life Sciences LLC.
Figures










References
-
- Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, Peltonen L, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, Peltonen L, Dermitzakis E, Schaffner SF, Yu F, Peltonen L, Dermitzakis E, Bonnen PE, Altshuler DM, Gibbs RA, de Bakker PI, Deloukas P, Gabriel SB, Gwilliam R, Hunt S, Inouye M, Jia X, Palotie A, Parkin M, Whittaker P, Yu F, Chang K, Hawes A, Lewis LR, Ren Y, Wheeler D, Gibbs RA, Muzny DM, Barnes C, Darvishi K, Hurles M, Korn JM, Kristiansson K, Lee C, McCarrol SA, Nemesh J, Dermitzakis E, Keinan A, Montgomery SB, Pollack S, Price AL, Soranzo N, Bonnen PE, Gibbs RA, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Keinan A, Price AL, Yu F, Anttila V, Brodeur W, Daly MJ, Leslie S, McVean G, Moutsianas L, Nguyen H, Schaffner SF, Zhang Q, Ghori MJ, McGinnis R, McLaren W, Pollack S, Price AL, Schaffner SF, Takeuchi F, Grossman SR, Shlyakhter I, Hostetter EB, Sabeti PC, Adebamowo CA, Foster MW, Gordon DR, Licinio J, Manca MC, Marshall PA, Matsuda I, Ngare D, Wang VO, Reddy D, Rotimi CN, Royal CD, Sharp RR, Zeng C, Brooks LD, McEwen JE, International HapMap 3 Consortium Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 2010;467:52–58. doi: 10.1038/nature09298. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Basty N, Liu Y, Cule M, Thomas EL, Bell JD, Whitcher B. Automated measurement of pancreatic fat and iron concentration using Multi-Echo and T1-Weighted MRI data. 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI); 2020. pp. 345–348. - DOI
-
- Buch S, Stickel F, Trépo E, Way M, Herrmann A, Nischalke HD, Brosch M, Rosendahl J, Berg T, Ridinger M, Rietschel M, McQuillin A, Frank J, Kiefer F, Schreiber S, Lieb W, Soyka M, Semmo N, Aigner E, Datz C, Schmelz R, Brückner S, Zeissig S, Stephan AM, Wodarz N, Devière J, Clumeck N, Sarrazin C, Lammert F, Gustot T, Deltenre P, Völzke H, Lerch MM, Mayerle J, Eyer F, Schafmayer C, Cichon S, Nöthen MM, Nothnagel M, Ellinghaus D, Huse K, Franke A, Zopf S, Hellerbrand C, Moreno C, Franchimont D, Morgan MY, Hampe J. A genome-wide association study confirms PNPLA3 and identifies TM6SF2 and MBOAT7 as risk loci for alcohol-related cirrhosis. Nature Genetics. 2015;47:1443–1448. doi: 10.1038/ng.3417. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bugianesi E, Bizzarri C, Rosso C, Mosca A, Panera N, Veraldi S, Dotta A, Giannone G, Raponi M, Cappa M, Alisi A, Nobili V. Low birthweight increases the likelihood of severe steatosis in pediatric Non-Alcoholic fatty liver disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology. 2017;112:1277–1286. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.140. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

