The use of cisplatin in patients after kidney transplantation with chronic renal insufficiency: Is the benefit higher than potential risks in therapy of non-seminomatous germ cell tumors?
- PMID: 34128899
- PMCID: PMC8213256
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026381
The use of cisplatin in patients after kidney transplantation with chronic renal insufficiency: Is the benefit higher than potential risks in therapy of non-seminomatous germ cell tumors?
Abstract
Rationale: The use of cisplatin in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is risky and depends on a number of factors. The optimal procedure in stage I of a non seminomatous germ cell tumor without proven lymphangioinvasion after orchiectomy is controversial and is the subject of a number of discussions due to the lack of randomized studies assessing individual treatment options. The adjuvant method of choice is surveillance or application of cisplatin-based chemotherapy with the risk of treatment related nephrotoxicity. Information about cisplatin safety in renal transplant patients is particularly limited. The aim of this paper is to share the experience with the application of adjuvant chemotherapy Bleomycin, Etoposide, Cisplatin (BEP) in high-risk patient with nonseminoma after kidney transplantation.
Patient concerns: We report a case report of rare group of high-risk patient with non-seminomatous germ cell testicular tumor (NSGCT) after kidney transplantation before application of adjuvant chemotherapy BEP. Patient presented with month-long discomfort in the scrotal area. Previously, he was treated with chronic kidney disease based on chronic glomerulonephritis, which was treated with repeated kidney transplantation.
Diagnosis: The ultrasound examination for a month-long discomfort in the scrotal area found a solid mass of the left testis. Radical inguinal orchiectomy confirmed NSGCT with the presence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI). Postoperative staging with computed tomography of the chest and abdomen did not show obvious dissemination of the disease.
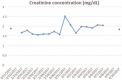
Interventions: Reducing original dose of chemotherapeutics according to the recommendations of the summary of product characteristics led to only a transient increase in creatinine levels.
Outcomes: The 5-year risk of relapse in surveillance was reduced to around 3% by applying cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
Lessons: Application of cisplatin-based chemotherapy is safe and effective in patients with CKD and in patients with a kidney transplant.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Tandstad T, Ståhl O, Håkansson U, et al. . One course of adjuvant BEP in clinical stage I nonseminoma mature and expanded results from the SWENOTECA group. Ann Oncol 2014;25:2167–72. - PubMed
-
- Divrik RT, Akdoğan B, Ozen H, Zorlu F. Outcomes of surveillance protocol of clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ cell tumors-is shift to risk adapted policy justified? J Urol 2006;176((4 pt 1)):1424–9. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Testicular Cancer (Version 1.2021). Available at: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/testicular.pdf. Accessed December 16, 2020.
-
- EAU Guidelines. Edn. presented at the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam; 2020. ISBN 978–94-92671-07-3.
-
- Ebewe Pharma Ges.m.b.H. Nfg. KG(2019) Cisplatin Ebewe 1 mg/ml Concentrate for Solution for Infusion SmPC. Available at: http://www.sukl.cz/modules/medication/detail.php?code=0189992&tab=texts (Accessed: March 20, 2017).[Article in Czech].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical