Clinical and echocardiographic findings in a cross-sectional study of HIV-infected adults in Enugu, Nigeria
- PMID: 34128946
- PMCID: PMC8756073
- DOI: 10.5830/CVJA-2020-065
Clinical and echocardiographic findings in a cross-sectional study of HIV-infected adults in Enugu, Nigeria
Abstract
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) are implicated in cardiovascular diseases. The objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical and echocardiographic findings in HIV-infected adults.
Methods: One hundred HIV subjects on HAART, 100 HAART-naïve patients and 100 controls were recruited in this cross-sectional study.
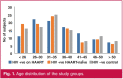
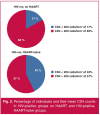
Results: Mean CD4 cell count was significantly higher in the HAART-exposed (408.43 ± 221.62) than the HAART-naïve groups (250.06 ± 154.26) (p < 0.001). Weight loss (49%), skin lesions (14%), body weakness (24%), oral thrush (10%) and lymphadenopathy (10%) were more prevalent in HAART-naïve patients (p < 0.05). Dimensions of aortic root (2.71 cm), left atrium (3.27 cm) and left ventricular mass index (79.95) were significantly higher in HIV-positive subjects on HAART (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Clinical features of HIV and the CD4 nadir were more prevalent in the HIV-positive, HAART-naïve subjects. Dimensions of the aortic root, left atrium and left ventricle were relatively larger in the HAART-exposed patients while wall thickness and ejection fraction were higher in the HAART-naïve subjects.
Keywords: CD4 cell; antiretroviral therapy; cardiovascular; dimension; echocardiography; human immunodeficiency virus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electrocardiographic findings in a cross-sectional study of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) patients in Enugu, south-east Nigeria.Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016 Jul/Aug;27(4):252-257. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2016-007. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2016. PMID: 27841913 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Pathologic Features of Kidney Disease in Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy-Naive and Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy-Experienced Patients at a Tertiary Health Facility in Maiduguri, Northeastern Nigeria.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2022 Jan-Feb;33(1):72-79. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.367828. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2022. PMID: 36647981
-
Prevalence of dyslipidemia among human immunodeficiency virus infected Nigerians.Ann Afr Med. 2013 Jan-Mar;12(1):24-8. doi: 10.4103/1596-3519.108246. Ann Afr Med. 2013. PMID: 23480991
-
Thymic function in HIV-infection.Dan Med J. 2013 Apr;60(4):B4622. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23651726 Review.
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus-associated Heart Disease in Nigerian Children: A Persistent and Difficult Clinical Challenge.Niger Postgrad Med J. 2025 Jan 1;32(1):14-18. doi: 10.4103/npmj.npmj_319_24. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Niger Postgrad Med J. 2025. PMID: 40091466 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of How To Reduce Morbidity in HIV Patients With Cardiovascular Diseases.Cureus. 2023 Feb 7;15(2):e34745. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34745. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36909130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathological features of papillary thyroid carcinoma in HIV-infected patients.Front Oncol. 2023 May 5;13:1071923. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1071923. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37213296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. Press release: new survey results indicate that Nigeria has an HIV prevalence of 1.4%. Available at: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/presscentre/pressreleaseandstatement... .
-
- The United States President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief 2019 Annual Report to Congress. https://www.state.gov/wp-content/ uploads/2019/09/PEPFAR2019ARC.pdf.
-
- Crum NF, Riffenburgh RH, Wegner S, Agan BK, Tasker SA, Spooner KM. et al. Comparisons of causes of death and mortality rates among HIV-infected persons: analysis of the pre-, early, and late HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy) eras. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;41:194–200. - PubMed
-
- Hooshyar D, Hanson DL, Wolfe M, Selik RM, Buskin SE, McNaghten AD. et al. Trends in perimortal conditions and mortality rates among HIV-infected patients. AIDS. 2007;21:2093–2100. - PubMed
-
- Ntsekhe M, Hakim J. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus infection on cardiovascular disease in Africa. Circulation. 2005;112:3602–3607. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials