Variability of acquisition phase of computed tomography angiography in acute ischemic stroke in a real-world scenario
- PMID: 34129068
- PMCID: PMC8660718
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-021-08084-5
Variability of acquisition phase of computed tomography angiography in acute ischemic stroke in a real-world scenario
Abstract
Objectives: The informative value of computed tomography angiography (CTA) depends on the contrast phase in the vessels which may differ depending on the level of local expertise.
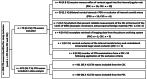
Methods: We retrospectively measured vessel contrast density from CTA scans in patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke to a comprehensive stroke center (CSC) or to one of eight primary stroke centers (PSC). CTAs were classified into arterial or venous phases as well as into 1 of 5 phases (early arterial, peak arterial, equilibrium, peak venous, and late venous).
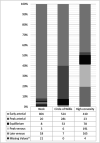
Results: Overall, n = 871 CTAs (CSC: n = 431 (49.5%); PSC: n = 440 (50.5%)) were included in the final analysis. A higher venous than arterial contrast density at the level of the circle of Willis was only rarely observed (overall n = 13 (1.5%); CSC: n = 3/431 (0.7%); PCS: n = 10/440 (2.3%); p = 0.09). CTAs acquired in the CSC showed more often an early arterial contrast phase (CSC: n = 371 (86.1%); PSC: n = 153 (34.8%), p < 0.01). Equilibrium contrast phase, i.e., a slightly stronger arterial contrast with clear venous contrast filling, was more frequent in CTAs from the PSCs (CSC: n = 6 (1.4%); PSC: n = 47 (10.7%); p < 0.01).
Conclusions: Despite different technical equipment and examination protocols, the overall number of CTAs with venous contrast was low and did not differ between the CSC and the PCSs. Differences between the further differentiated contrast phases indicate potential for further improvement of CTA acquisition protocols.
Key points: • Despite different technical equipment and examination protocols in the diagnostic workup of acute ischemic stroke, the total number of computed tomography angiography (CTA) with venous contrast was low (n = 13/871; 1.5%). • A higher venous than arterial contrast density at the level of the circle of Willis was not more frequent in CTAs from the centers with a high patient volume (comprehensive stroke center) compared to the hospital with lower patient volume (primary stroke centers). • Differences between the further differentiated contrast phases indicate that there is potential for further improvement of CTA acquisition protocols.
Keywords: Computed tomography angiography; Contrast media; Stroke.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Pfaff reports personal fees from Stryker outside the submitted work.
Ms. Füssel, Mr. Harlan, and Dr. Hubert have nothing to disclose.
The authors of this manuscript declare relationships with the following companies: Dr. Bendszus reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, BBraun, Vascular Dynamics, Bayer, Merck, Teva, Grifols, and Springer; grants and personal fees from Novartis and Guerbet; grants from Siemens, Hopp Foundation, from DFG, European Union, and Stryker, outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantification of infarct core signal using CT imaging in acute ischemic stroke.Neuroimage Clin. 2022;34:102998. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.102998. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Neuroimage Clin. 2022. PMID: 35378498 Free PMC article.
-
Variability of computed tomography angiography coverage of lung parenchyma in acute stroke.Neurol Res Pract. 2021 Mar 2;3(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s42466-021-00109-0. Neurol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33648607 Free PMC article.
-
Delay of late-venous phase cortical vein filling in acute ischemic stroke patients: Associations with collateral status.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017 Feb;37(2):671-682. doi: 10.1177/0271678X16637611. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017. PMID: 26965242 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of single-phase CT angiography in detecting large vessel occlusion in ischemic stroke: A systematic review.Eur J Radiol. 2021 Jan;134:109458. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.109458. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Eur J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33302028
-
Yield of Computed Tomography (CT) Angiography in Patients with Acute Headache, Normal Neurological Examination, and Normal Non Contrast CT: A Meta-Analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Apr;27(4):1077-1084. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Dec 23. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29277281 Review.
Cited by
-
Structured reporting of computed tomography in the staging of colon cancer: a Delphi consensus proposal.Radiol Med. 2022 Jan;127(1):21-29. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01418-9. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 34741722 Free PMC article.
-
Structured Reporting of Computed Tomography in the Staging of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Delphi Consensus Proposal.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 30;12:748944. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.748944. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34917023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50:e344–e418 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

