[Neuropathology of dementia]
- PMID: 34129141
- PMCID: PMC8397629
- DOI: 10.1007/s10354-021-00848-4
[Neuropathology of dementia]
Abstract
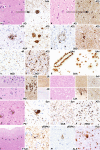
Dementia is the clinical consequence of various neurological disorders with a multitude of etiologies. Precise knowledge of the underlying pathologies is essential for an accurate treatment of patients and for the development of suitable disease biomarkers. A definite diagnosis of many of the disorders, particularly for neurodegenerative ones, can only be made after a thorough postmortem neuropathological examination. This highlights the importance of performing a brain autopsy and the relevance of a close interaction between clinicians, neuroimaging disciplines and neuropathologists as well as with basic researchers. This article aims to give a brief overview on the neuropathology of dementia focusing on neurodegenerative diseases, to further facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration.
Demenz ist die klinische Folge verschiedener neurologischer Erkrankungen mit einer Vielzahl von Ätiologien. Dabei ist die genaue Kenntnis der zugrunde liegenden pathologischen Veränderungen entscheidend für die passgenaue Versorgung der Patienten und für die Entwicklung geeigneter Krankheitsbiomarker. Eine definitive Diagnose vieler dieser Erkrankungen, insbesondere der neurodegenerativen Formen, kann nur nach gründlicher postmortaler neuropathologischer Untersuchung gestellt werden. Dies unterstreicht die Wichtigkeit der Durchführung einer Gehirnautopsie und die Relevanz einer engen Zusammenarbeit zwischen Klinikern, Neuroradiologen und Neuropathologen sowie mit Grundlagenforschern. Ziel der vorliegenden Arbeit ist es, einen kurzen Überblick über die Neuropathologie der Demenz mit Schwerpunkt auf neurodegenerative Erkrankungen zu geben, um die interdisziplinäre Zusammenarbeit weiter zu fördern.
Keywords: Biomarker; Dementia; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathology; Proteinopathies.
© 2021. The Author(s).
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical