Metallo-β-lactamases in the Age of Multidrug Resistance: From Structure and Mechanism to Evolution, Dissemination, and Inhibitor Design
- PMID: 34129337
- PMCID: PMC9062786
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00138
Metallo-β-lactamases in the Age of Multidrug Resistance: From Structure and Mechanism to Evolution, Dissemination, and Inhibitor Design
Abstract
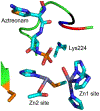
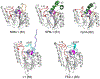
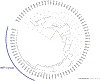
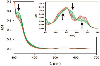
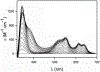
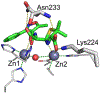
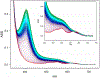
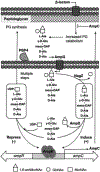
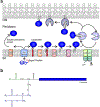
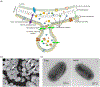
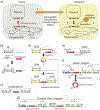
Antimicrobial resistance is one of the major problems in current practical medicine. The spread of genes coding for resistance determinants among bacteria challenges the use of approved antibiotics, narrowing the options for treatment. Resistance to carbapenems, last resort antibiotics, is a major concern. Metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) hydrolyze carbapenems, penicillins, and cephalosporins, becoming central to this problem. These enzymes diverge with respect to serine-β-lactamases by exhibiting a different fold, active site, and catalytic features. Elucidating their catalytic mechanism has been a big challenge in the field that has limited the development of useful inhibitors. This review covers exhaustively the details of the active-site chemistries, the diversity of MBL alleles, the catalytic mechanism against different substrates, and how this information has helped developing inhibitors. We also discuss here different aspects critical to understand the success of MBLs in conferring resistance: the molecular determinants of their dissemination, their cell physiology, from the biogenesis to the processing involved in the transit to the periplasm, and the uptake of the Zn(II) ions upon metal starvation conditions, such as those encountered during an infection. In this regard, the chemical, biochemical and microbiological aspects provide an integrative view of the current knowledge of MBLs.
Figures



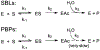





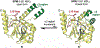






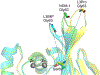




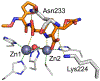

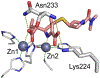








References
-
- Fleming A On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of a Penicillium, with Special Reference to Their Use in the Isolation of B. Influenzæ. British Journal of Experimental Pathology 1929, 10, 226–236.
-
- Fleming A Streptococcal Meningitis Treated with Penicillin.: Measurement of Bacteriostatic Power of Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid. The Lancet 1943, 242, 434–438.
-
- Abraham EP History of B-Lactam Antibiotics. In Antibiotics: Containing the Beta-Lactam Structure, Demain AL; Solomon NA, Eds. Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 1983; pp 1–14.
-
- Bennett JW; Chung KT Alexander Fleming and the Discovery of Penicillin. Adv. Appl. Microbiol 2001, 49, 163–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

