Study on the influence of advanced treatment processes on the surface properties of polylactic acid for a bio-based circular economy for plastics
- PMID: 34130189
- PMCID: PMC8209739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105627
Study on the influence of advanced treatment processes on the surface properties of polylactic acid for a bio-based circular economy for plastics
Abstract
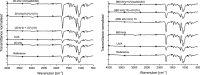
New biotechnological processes using microorganisms and/or enzymes to convert carbonaceous resources, either biomass or depolymerized plastics into a broad range of different bioproducts are recognized for their high potential for reduced energy consumption and reduced GHG emissions. However, the hydrophobicity, high molecular weight, chemical and structural composition of most of them hinders their biodegradation. A solution to reduce the impact of non-biodegradable polymers spread in the environment would be to make them biodegradable. Different approaches are evaluated for enhancing their biodegradation. The aim of this work is to develop and optimize the ultrasonication (US) and UV photodegradation and their combination as well as dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma as pre-treatment technologies, which change surface properties and enhance the biodegradation of plastic by surface oxidation and thus helping bacteria to dock on them. Polylactic acid (PLA) has been chosen as a model polymer to investigate its surface degradation by US, UV, and DBD plasma using surface characterization methods like X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Confocal Laser Microscopy (CLSM), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) as well as FT-IR and drop contour analysis. Both US and UV affect the surface properties substantially by eliminating the oxygen content of the polymer but in a different way, while plasma oxidizes the surface.
Keywords: AFM; CLSM; DBD plasma; FTIR; Micro-plastics; Pre-treatment of polymers; Sonochemistry; UV photochemistry; XPS.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Laccase driven biocatalytic oxidation to reduce polymeric surface hydrophobicity: An effective pre-treatment strategy to enhance biofilm mediated degradation of polyethylene and polycarbonate plastics.Sci Total Environ. 2023 Dec 15;904:166721. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166721. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 37673259
-
Marine-Derived Actinomycetes: Biodegradation of Plastics and Formation of PHA Bioplastics-A Circular Bioeconomy Approach.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 1;20(12):760. doi: 10.3390/md20120760. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36547907 Free PMC article.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Atmospheric pressure cold plasma versus wet-chemical surface treatments for carboxyl functionalization of polylactic acid: A first step toward covalent immobilization of bioactive molecules.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020 May;189:110847. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.110847. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020. PMID: 32086024
-
The Closure of the Cycle: Enzymatic Synthesis and Functionalization of Bio-Based Polyesters.Trends Biotechnol. 2016 Apr;34(4):316-328. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.12.009. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Trends Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26806112 Review.
Cited by
-
Eco-Design of Polymer Matrix Composite Parts: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Sep 2;15(17):3634. doi: 10.3390/polym15173634. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37688260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Catalyst-Free Amino-Yne Click Reaction: An Efficient Way for Immobilizing Amoxicillin onto Polymeric Surfaces.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jan 15;16(2):246. doi: 10.3390/polym16020246. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257045 Free PMC article.
-
An easy and simple method for the immobilization of dyes through click reactions: activated alkyne, copper not needed.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 30;14(20):14289-14295. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01776e. eCollection 2024 Apr 25. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38690116 Free PMC article.
-
Study of PLA pre-treatment, enzymatic and model-compost degradation, and valorization of degradation products to bacterial nanocellulose.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Apr 17;39(6):161. doi: 10.1007/s11274-023-03605-4. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37067621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bröring S., Laibach N., Wustmans M. Innovation Types in the bioeconomy. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020;266:121939. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121939. - DOI
-
- Loizia, P., Neofytou, N., Zorpas, A.A. 2018 The concept of circular economy in food waste management for the optimization of energy production through UASB reactor Environmental Science and Pollution research, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3519-4. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien M., Wechsler D., Bringezu S., Schaldach R. Toward a systemic monitoring of the European bioeconomy: gaps, needs and the integration of sustainability indicators and targets for global land use. Land Use Pol. 2017;66:162–171. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.04.047. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

