Review of the measles epidemic in children from Central Eastern Europe in the third millennium
- PMID: 34131439
- PMCID: PMC8193220
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10248
Review of the measles epidemic in children from Central Eastern Europe in the third millennium
Abstract
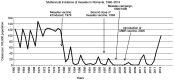
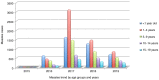
Measles is an extremely contagious viral disease. Even though a safe vaccine exists for this disease, it remains one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity in infants and young children. We aimed to create a retrospective descriptive study in which to analyze the evolution of the measles epidemic at the European level. The documentation was carried out using European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and World Health Organization (WHO) statistics. At the same time, we present the epidemic's evolution in Romania, using data provided by the Romanian National Institute of Public Health and Ministry of Health. European statistical data indicate a high number of patients diagnosed with measles both among children and adults. All European countries benefit from the measles vaccination in the form of the measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) trivaccine included in their National Vaccination Programme. The vaccination schedule varies from country to country. In the vaccination scheme, most European countries include two doses of the MMR vaccine among the pediatric population. Romania registered a limited number of cases of measles between 1980 and 2015 following the introduction of the measles vaccination in the National Vaccination Programme. Since 2005, the Romanian vaccination schedule includes two doses of MMR trivaccine, administered at 12 months and at 6-7 years. After 2015, as a result of a significant decrease in the number of vaccinated children, Romania is facing a major increase in the cases of measles. Consecutively, a measles epidemic was declared in 2016 and an additional dose of mandatory MMR trivaccine was introduced at the age of 9 months. After 4 years of this schedule of administration, starting with August 2020, the additional dose of MMR administered during infancy has been discontinued. We propose an analysis of the factors that influenced the downward evolution of the measles epidemic in Romania at the beginning of the third millennium. Issues related to the limitation of interpersonal contact in the context of the social distancing imposed by the Sars-CoV-2 virus pandemic are discussed. We consider necessary a detailed documentation of the percentage of new disease cases that will appear in the pediatric population in the near future, in the context of the resumption of daily activity after the reopening of nurseries, kindergartens and schools.
Keywords: Central-East Europe; Romania; children; measles; vaccination.
Copyright: © Davitoiu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests exist with regard to the publication of the descriptive study.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization: Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals on Measles, 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/measles/en/.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: ECDC. Monthly measles and rubella monitoring report, 2020. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/measles-rubella....
-
- Guglielmi G. Measles erases immune ‘memory’ for other diseases. Nature: Oct 31, 2019 (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-03324-7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
