Serum fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) as a potential biomarker of inflammation in psoriasis
- PMID: 34131888
- PMCID: PMC8260421
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-021-06461-3
Serum fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) as a potential biomarker of inflammation in psoriasis
Abstract
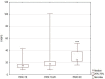
Fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) is elevated in psoriatic keratinocytes and could be involved in systemic metabolic disturbances in psoriasis. The aim of the study was to evaluate serum FABP5 in obese and non-obese psoriatic patients, to assess the relationship between FABP5 and the duration, severity of the disease, inflammatory and metabolic markers and influence of treatment with narrowband-ultraviolet B (NB-UVB). Seventy-four patients (30 treated with NB-UVB) with psoriasis were enrolled in the study. The serum concentrations of FABP5 were measured using Human FABP5 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay kit. Serum fatty acids were measured by gas-liquid chromatography. Serum FABP5 levels in psoriatic patients were higher versus control group (P < 0.001). FABP5 in patients with PASI > 20 was higher compared to the mild group (PASI < 10) (P < 0.001) and serum FABP5 correlated positively with PASI score (r = 0.41, P < 0.001). There was also positive correlation between FABP5 and basic inflammation indices. Decrease of PASI after NB-UVB treatment (P < 0.001) was observed and accompanied by decrease of the serum FABP5 (P = 0.007). FABP5 is a potential marker of psoriasis, its severity and clinical outcome after therapy with NB-UVB. FABP5 may reflect metabolic disturbances in psoriatic patients.
Keywords: Epidermal fatty acid binding protein; Fatty acid binding protein 5; Lipid disturbances; Metabolic syndrome; Narrowband—ultraviolet B; Psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Galectin3 levels in psoriatic patients treated by narrow-band UVB phototherapy.J Dermatolog Treat. 2020 Dec;31(8):758-762. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1670778. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020. PMID: 31557066
-
The Effect of Phototherapy on Systemic Inflammation Measured with Serum Vitamin D-Binding Protein and hsCRP in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 8;25(16):8632. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168632. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201319 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis therapy and cardiovascular risk factors: a 12-week follow-up study.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010 Dec 1;11(6):423-32. doi: 10.2165/11319310-000000000-00000. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20429617
-
Narrowband ultraviolet B versus psoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy for severe plaque psoriasis: an Indian perspective.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011 Mar;36(2):169-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03874.x. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 20545955 Review.
-
Effects of Narrow Band Ultraviolet B on Serum Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Interleukin-8 in Patients with Psoriasis.Am J Ther. 2016 May-Jun;23(3):e655-62. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000330. Am J Ther. 2016. PMID: 26308328 Review.
Cited by
-
Fatty Acid-Binding Proteins in Psoriasis-A Review.Metabolites. 2022 Sep 3;12(9):833. doi: 10.3390/metabo12090833. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36144237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal lipid metabolism in epidermal Langerhans cells mediates psoriasis-like dermatitis.JCI Insight. 2022 Jul 8;7(13):e150223. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150223. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35801590 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell sequencing analysis and multiple machine-learning models revealed the cellular crosstalk of dendritic cells and identified FABP5 and KLRB1 as novel biomarkers for psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1374763. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1374763. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596682 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel biomarkers related to pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis based on integrated analysis of weighted gene co-expression network analysis and LASSO.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0317666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317666. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40560938 Free PMC article.
-
Hormone correction of dysfunctional metabolic gene expression in stem cell-derived liver tissue.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Mar 11;16(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04238-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40069876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strand V, Gonçalves J, Hickling TP, Jones HJ, Marshall L, Isaacs JD. Immunogenicity of biosimilars for rheumatic diseases, plaque psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease: a review from clinical trials and regulatory documents. BioDrugs. 2020;34:27–37. doi: 10.1007/s40259-019-00394-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Magdaleno-Tapial J, Valenzuela-Oñate C, Ortiz-Salvador JM, Martínez-Doménech A, García-Legaz-Martínez M, Alonso-Carpio M, Tamarit-García JJ, et al. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver and liver fibrosis in patients with moderate-severe psoriasis: a cross-sectional cohort study. Australas J Dermatol. 2020;61:105–109. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13175. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

