Non-Infectious Granulomatous Lung Disease: Imaging Findings with Pathologic Correlation
- PMID: 34132073
- PMCID: PMC8316771
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2020.1082
Non-Infectious Granulomatous Lung Disease: Imaging Findings with Pathologic Correlation
Abstract
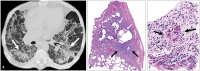
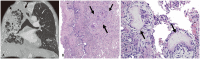
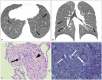
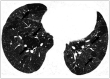
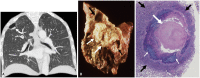
Non-infectious granulomatous lung disease represents a diverse group of disorders characterized by pulmonary opacities associated with granulomatous inflammation, a relatively nonspecific finding commonly encountered by pathologists. Some lesions may present a diagnostic challenge because of nonspecific imaging features; however, recognition of the various imaging manifestations of these disorders in conjunction with patients' clinical history, such as age, symptom onset and duration, immune status, and presence of asthma or cutaneous lesions, is imperative for narrowing the differential diagnosis and determining appropriate management of this rare group of disorders. In this pictorial review, we describe the pathologic findings of various non-infectious granulomatous lung diseases as well as the radiologic features and high-resolution computed tomography imaging features.
Keywords: Granulomatous lung disease; High-resolution computed tomography; Lung parenchyma; Non-infectious granulomatosis; Radiography.
Copyright © 2021 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



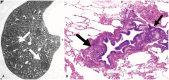
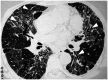
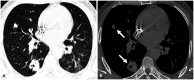

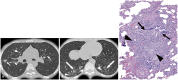

Similar articles
-
CT of noninfectious granulomatous lung disease.Radiol Clin North Am. 2001 Nov;39(6):1189-209, vi. doi: 10.1016/s0033-8389(05)70338-9. Radiol Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11699668 Review.
-
[Granulomatous diseases and pathogenic microorganism].Kekkaku. 2008 Feb;83(2):115-30. Kekkaku. 2008. PMID: 18326339 Japanese.
-
Idiopathic granulomatous bronchitis. An unusual form of known granulomatous lung diseases or an unknown disease?Sarcoidosis. 1992 Mar;9(1):60-6. Sarcoidosis. 1992. PMID: 1344046
-
The spectrum of eosinophilic lung disease: radiologic findings.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997 Nov-Dec;21(6):920-30. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199711000-00015. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1997. PMID: 9386285
-
[Computed tomography findings in pulmonary involvement of Wegener's granulomatosis: pictorial review].Tuberk Toraks. 2015;63(4):257-64. doi: 10.5578/tt.9986. Tuberk Toraks. 2015. PMID: 26963309 Review. Turkish.
Cited by
-
Systematic review of the diagnostic role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in sarcoidosis.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023 Mar 28;40(1):e2023008. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v40i1.13824. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2023. PMID: 36975052 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of cough-related quality of life in interstitial lung diseases.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03218-z. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39210302 Free PMC article.
-
Noninfectious Granulomatous Lung Disease: Radiological Findings and Differential Diagnosis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 23;14(2):134. doi: 10.3390/jpm14020134. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38392568 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Myers JL, Tazelaar HD. Challenges in pulmonary fibrosis: 6 · Problematic granulomatous lung disease. Thorax. 2008;63:78–84. - PubMed
-
- Freundlich IM, Capp MP. Granulomatous disease of the lungs. Radiol Clin North Am. 1973;11:295–316. - PubMed
-
- El-Zammar OA, Katzenstein AL. Pathological diagnosis of granulomatous lung disease: a review. Histopathology. 2007;50:289–310. - PubMed
-
- Colby TV, Specks U. Wegener's granulomatosis in the 1990s--a pulmonary pathologist's perspective. Monogr Pathol. 1993;(36):195–218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

