Pharmacokinetics of preoperative intraperitoneal 5-FU in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34132895
- PMCID: PMC8367903
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-021-04318-x
Pharmacokinetics of preoperative intraperitoneal 5-FU in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
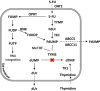
Purpose: The aim was to investigate the pharmacokinetics of preoperatively administered intraperitoneal (IP) 5-FU in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) by analyzing levels of 5-FU and target metabolites in peritoneal fluid, plasma, liver, lymph nodes, pancreatic tumour, and pancreatic tissue. These results were correlated to expression of genes encoding enzymes of the 5-FU pathway and cell membrane transporters of 5-FU and FdUMP.
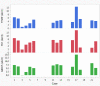
Methods: Twenty-two patients with PDAC were treated with IP 5-FU before surgery. The postoperative treatment followed a routine clinical protocol. 5-FU and its metabolites were analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The expression of genes encoding enzymes and transporters in the 5-FU pathway was analyzed by qPCR.
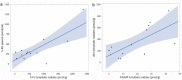
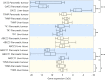
Results: After IP treatment, 5-FU could be detected in plasma, lymph nodes, liver, pancreatic tumour, and pancreatic tissue. The highest 5-FU concentration was found in the liver, also expressing high levels of the 5-FU transporter OAT2. 5-FU was converted to active FdUMP in all tissues and the highest concentration was measured in lymph nodes, liver and pancreatic tumour (18.5, 6.1 and 6.7 pmol/g, respectively). There was a correlation between the FdUMP and dUr levels in lymph nodes (r = 0.70, p = 0.0076). In tumours, there was an association between OAT2 expression and FdUMP concentration.
Conclusion: The study shows uptake of IP 5-FU and drug metabolism to active FdUMP in pancreatic tumour, liver, and lymph nodes. Extended studies are warranted to evaluate the IP route for 5-FU administration in PDAC patients.
Keywords: 5-Fluorouracil; Gene expression; Intraperitoneal chemotherapy; Pancreatic cancer; Pharmacokinetics.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No affiliation or financial involvement in any organization or entity with a direct financial interest in the subject, matter or materials discussed in the manuscript exists.
Figures
References
-
- Collaborators GBDPC The global, regional, and national burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4(12):934–947. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30347-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

