Patient Experiences of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Findings From a Systematic Review, Meta-Summary, and Meta-Synthesis
- PMID: 34133081
- PMCID: PMC9796081
- DOI: 10.1002/acr.24639
Patient Experiences of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Findings From a Systematic Review, Meta-Summary, and Meta-Synthesis
Abstract
Objective: To explore the experience of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
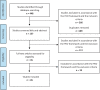
Methods: A systematic review of qualitative studies published in English in the past 10 years and identified through the PubMed, CINAHL, Scopus, and Web of Science databases was performed following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. The methodologic quality of each included study was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Screening Programme tool. Study findings were then subjected to a meta-summary and meta-synthesis.
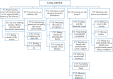
Results: Twenty-six studies with a good overall methodologic quality were included, documenting the experience of 565 adult patients (95% women). A total of 17 codes emerged, summarizing the life experience of SLE patients; the most and least frequent codes in the meta-summary were "feeling not as I usually do" (69.2%) and "having wishes" (7.7%). The codes were then categorized into 5 main themes, summarizing the experience of living with SLE: 1) "experiencing waves of emotions due to the unpredictable nature of the disease," 2) "trying to live an ordinary life," 3) "listening to and obeying the body's limitations," 4) "reviewing my life projects," and 5) "dealing with future uncertainties."
Conclusion: Several qualitative studies have been published to date using good methodologic approaches. According to the findings, SLE negatively impacts patient experiences by affecting multiple dimensions of their daily lives, with fatigue and pain as the most frequent symptoms.
© 2021 The Authors. Arthritis Care & Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Living with systemic lupus erythematosus in South Africa: a bitter pill to swallow.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019 Apr 16;17(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12955-019-1132-y. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019. PMID: 30992020 Free PMC article.
-
A Transcultural Perspective of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Related Fatigue: Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis.Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2022 Sep 15;6(1):e39132. doi: 10.2196/39132. Asian Pac Isl Nurs J. 2022. PMID: 36648284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
The experience of individuals placed in quarantine: A systematic review, meta-summary, and meta-synthesis.Public Health Nurs. 2021 Jul;38(4):627-636. doi: 10.1111/phn.12910. Epub 2021 May 4. Public Health Nurs. 2021. PMID: 33942378 Free PMC article.
-
The Type 1 & 2 systemic lupus erythematosus model: Perspectives of people living with systemic lupus erythematosus.Lupus. 2024 Mar;33(3):266-272. doi: 10.1177/09612033241228343. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Lupus. 2024. PMID: 38238905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Canadian patient experiences of lupus nephritis: a qualitative analysis.Lupus Sci Med. 2023 Dec 9;10(2):e000982. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2023-000982. Lupus Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 38087643 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Disease-Related Experiences of TikTok Users With Lupus Erythematosus: Qualitative and Content Analysis.JMIR Infodemiology. 2024 Apr 17;4:e51211. doi: 10.2196/51211. JMIR Infodemiology. 2024. PMID: 38631030 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual and reproductive health from the perspective of patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases in Mexico: a qualitative study.BMJ Open. 2025 Jan 28;15(1):e086351. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086351. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 39880419 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers, Facilitators, and Preferences for Mental Health Services Among Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Qualitative Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024 Jul;76(7):914-925. doi: 10.1002/acr.25321. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38433607 Free PMC article.
-
Vagus nerve stimulation as a novel treatment for systemic lupus erythematous: study protocol for a randomised, parallel-group, sham-controlled investigator-initiated clinical trial, the SLE-VNS study.BMJ Open. 2022 Sep 20;12(9):e064552. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064552. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36127117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves VL, Carniel AQ, Costallat LT, Turato ER. Meanings of the sickening process for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of the literature. Rev Bras Reumatol 2015;55:522–7. - PubMed
-
- Mazzoni D, Cicognani E. Problematic social support from patients' perspective: the case of systemic lupus erythematosus. Soc Work Health Care 2014;53:435–45. - PubMed
-
- Robinson M, Sheets Cook S, Currie LM. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a genetic review for advanced practice nurses. J Am Acad Nurse Pract 2011;23:629–37. - PubMed
-
- Larsen JL, Hall EO, Jacobsen S, Birkelund R. The existential experience of everyday life with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Adv Nurs 2018;74:1170–9. - PubMed
-
- Mazzoni D, Cicognani E. Sharing experiences and social support requests in an Internet forum for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Health Psychol 2014;19:689–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

