Identification of RNA binding protein interacting with circular RNA and hub candidate network for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 34133325
- PMCID: PMC8266373
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203139
Identification of RNA binding protein interacting with circular RNA and hub candidate network for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
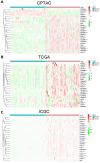
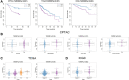
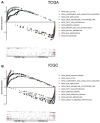
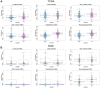
The interaction between RNA binding protein (RBP) and circular RNA (circRNA) is important for the regulation of tumor progression. This study aimed to identify the RBP-circRNA network in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). 22 differentially expressed (DE) circRNAs in HCC were screened out from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database and their binding RBPs were predicted by Circular RNA Interactome. Among them, 17 DERBPs, which were commonly dysregulated in HCC from The Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC), The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) projects, were utilized to construct the RBP-circRNA network. Through survival analysis, we found TARDBP was the only prognostic RBP for HCC in CPTAC, TCGA and ICGC projects. High expression of TARDBP was correlated with high grade, advanced stage and low macrophage infiltration of HCC. Additionally, gene set enrichment analysis showed that dysregulated TARDBP might be involved in some pathways related to the HCC pathogenesis. Therefore, a hub RBP-circRNA network was generated based on TARDBP. RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA pull-down confirmed that hsa_circ_0004913 binds to TARDBP. These findings indicated certain RBP-circRNA regulatory network potentially involved in the pathogenesis of HCC, which provides novel insights into the mechanism study and biomarker identification for HCC.
Keywords: RNA binding protein; circular RNA; hepatocellular carcinoma; regulatory network.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of the competing endogenous circRNA-lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network and identification of a novel potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 28;13(12):15990-16008. doi: 10.18632/aging.203056. Epub 2021 May 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34049287 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel RNA Binding Proteins Influencing Circular RNA Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 12;22(14):7477. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147477. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299096 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of circular RNA-microRNA-messenger RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Jan;35(1):157-164. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14762. Epub 2019 Jul 18. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31222831
-
The functional roles, cross-talk and clinical implications of m6A modification and circRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jul 22;17(12):3059-3079. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.62767. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34421350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress and prospects of circular RNAs in Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel insights into their function.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4408-4422. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26154. Epub 2017 Sep 28. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28833094 Review.
Cited by
-
CircRNA-mTOR Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Lenvatinib Resistance Through the PSIP1/c-Myc Axis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 May;12(20):e2410591. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410591. Epub 2025 Apr 15. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40231634 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation and oncogenic activities of ubiquitin specific peptidase 2a in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 15;13(6):2392-2409. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37424823 Free PMC article.
-
Dual inhibition of FAS and HAS2/3 by 4-MU in Realgar-Coptis chinensis unveils a metabolic checkpoint for liver cancer therapy.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025 Aug 21;15(1):56. doi: 10.1007/s13659-025-00540-9. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2025. PMID: 40839202
-
DDX1 is a prognostic biomarker and correlates with immune infiltrations in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Immunol. 2022 Nov 30;23(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12865-022-00533-0. BMC Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36451087 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel circRNA hsa_circRNA_002178 as a Diagnostic Marker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Enhances Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Tumor Growth by Stabilizing SRSF1 Expression.J Oncol. 2022 Aug 27;2022:4184034. doi: 10.1155/2022/4184034. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36065311 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

