Head-mounted microendoscopic calcium imaging in dorsal premotor cortex of behaving rhesus macaque
- PMID: 34133921
- PMCID: PMC8236375
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109239
Head-mounted microendoscopic calcium imaging in dorsal premotor cortex of behaving rhesus macaque
Abstract
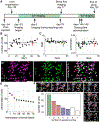
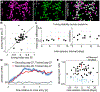
Microendoscopic calcium imaging with one-photon miniature microscopes enables unprecedented readout of neural circuit dynamics during active behavior in rodents. In this study, we describe successful application of this technology in the rhesus macaque, demonstrating plug-and-play, head-mounted recordings of cellular-resolution calcium dynamics from large populations of neurons simultaneously in bilateral dorsal premotor cortices during performance of a naturalistic motor reach task. Imaging is stable over several months, allowing us to longitudinally track individual neurons and monitor their relationship to motor behavior over time. We observe neuronal calcium dynamics selective for reach direction, which we could use to decode the animal's trial-by-trial motor behavior. This work establishes head-mounted microendoscopic calcium imaging in macaques as a powerful approach for studying the neural circuit mechanisms underlying complex and clinically relevant behaviors, and it promises to greatly advance our understanding of human brain function, as well as its dysfunction in neurological disease.
Keywords: GCaMP; GRIN lens; arm reach; calcium imaging; decoding behavior; longitudinal tracking; macaque; microendoscopy; miniscope; premotor cortex.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.B., P.S.X., and J.J.N. are paid employees of Inscopix, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Windows and periscopes into primate behavior.Cell Rep. 2021 Jul 20;36(3):109435. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109435. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34289362
-
Optical deep-cortex exploration in behaving rhesus macaques.Nat Commun. 2021 Aug 2;12(1):4656. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24988-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34341349 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Dendritic calcium signals in rhesus macaque motor cortex drive an optical brain-computer interface.Nat Commun. 2021 Jun 17;12(1):3689. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23884-5. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34140486 Free PMC article.
-
Microendoscopic calcium imaging of the primary visual cortex of behaving macaques.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 23;11(1):17021. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96532-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34426639 Free PMC article.
-
Miniscope GRIN Lens System for Calcium Imaging of Neuronal Activity from Deep Brain Structures in Behaving Animals.Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2019 Jan;86(1):e56. doi: 10.1002/cpns.56. Epub 2018 Oct 13. Curr Protoc Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30315730 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging neuronal populations in behaving rodents: paradigms for studying neural circuits underlying behavior in the mammalian cortex.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 6;33(45):17631-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3255-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Miniature microscopes for large-scale imaging of neuronal activity in freely behaving rodents.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015 Jun;32:141-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 16. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25951292 Review.
Cited by
-
Miniature microscopes for manipulating and recording in vivo brain activity.Microscopy (Oxf). 2021 Oct 5;70(5):399-414. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfab028. Microscopy (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 34283242 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing advances in the future of primate neuroscience research.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022 Dec 13;4:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2022.100064. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36582401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Open-Source Real-Time Motion Correction Plug-In for Single-Photon Calcium Imaging of Head-Mounted Microscopy.Front Neural Circuits. 2022 Jun 24;16:891825. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2022.891825. eCollection 2022. Front Neural Circuits. 2022. PMID: 35814484 Free PMC article.
-
Motor actions are spatially organized in motor and dorsal premotor cortex.Elife. 2023 Oct 19;12:e83196. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83196. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37855376 Free PMC article.
-
Low frequency independent components: Internal neuromarkers linking cortical LFPs to behavior.iScience. 2023 Oct 28;27(2):108310. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108310. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38303697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arieli A, Grinvald A, and Slovin H (2002). Dural substitute for long-term imaging of cortical activity in behaving monkeys and its clinical implications. J. Neurosci. Methods 114, 119–133. - PubMed
-
- Capitanio JP, and Emborg ME (2008). Contributions of non-human primates to neuroscience research. Lancet 371, 1126–1135. - PubMed
-
- Chen LM, Heider B, Williams GV, Healy FL, Ramsden BM, and Roe AW (2002). A chamber and artificial dura method for long-term optical imaging in the monkey. J. Neurosci. Methods 113, 41–49. - PubMed

