Efficacy and safety assessment of prolonged maintenance with subcutaneous rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma: results of the phase III MabCute study
- PMID: 34134469
- PMCID: PMC8804572
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2020.274803
Efficacy and safety assessment of prolonged maintenance with subcutaneous rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma: results of the phase III MabCute study
Abstract
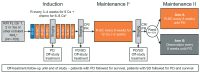
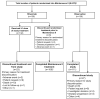
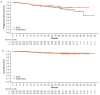
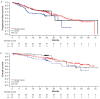
Rituximab plus chemotherapy induction followed by rituximab maintenance for up to 2 years confers a long-term benefit in terms of progression-free survival in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. It is not known whether further prolonged maintenance with rituximab provides additional benefit. The phase III MabCute study enrolled 692 patients with relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Patients who responded to induction with rituximab plus chemotherapy and were still responding after up to 2 years' initial maintenance with subcutaneous rituximab were randomized to extended maintenance with subcutaneous rituximab (n=138) or observation only (n=138). The primary endpoint of investigator-assessed progression-free survival in the randomized population was un-addressed by the end of study because of an insufficient number of events (129 events were needed for 80% power at 5% significance if approximately 330 patients were randomized). In total, there were 46 progression-free survival events, 19 and 27 in the rituximab and observation arms, respectively (P=0.410 by stratified log-rank test; hazard ratio 0.76 [95% confidence interval: 0.37- 1.53]). The median progression-free survival was not reached in either randomized arm. There were no new safety signals; however, adverse events were seen slightly more frequently with rituximab than with observation during extended maintenance. Maintenance for up to 2 years with rituximab after response to initial induction therefore remains the standard of care in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent non- Hodgkin lymphoma. (Clinicaltrials.gov identifier: NCT01461928).
Figures
Comment in
-
Too much and not enough: revisiting maintenance rituximab in indolent lymphomas.Haematologica. 2022 Feb 1;107(2):353-354. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.279101. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 34134474 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ninkovic S, Lambert J. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Medicine. 2017;45(5):297-304.
-
- Shankland KR, Armitage JO, Hancock BW. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet. 2012;380 (9844):848-857. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Ghielmini M, Rule S, et al. . Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow- up. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(3):298-308. - PubMed
-
- Kastritis E, Leblond V, Dimopoulos MA, et al. . Waldenström’s macroglobulinaemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(Suppl 4):iv41-iv50. - PubMed
-
- Tilly H, Gomes da Silva M, Vitolo U, et al. . Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(Suppl 5):v116-125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

