Development of a complex arts-based intervention for patients with end-stage kidney disease whilst receiving haemodialysis
- PMID: 34134778
- PMCID: PMC8207758
- DOI: 10.1186/s40814-021-00868-2
Development of a complex arts-based intervention for patients with end-stage kidney disease whilst receiving haemodialysis
Abstract
Background: Patients with end-stage kidney disease who receive haemodialysis experience a protracted treatment regimen that can result in an increased risk of depression and anxiety. Arts-based interventions could address this unique issue; however, no arts-based interventions have been developed for delivery within a haemodialysis unit and evaluation within a randomised controlled trials (RCTs).
Aim: To develop a complex arts-based intervention for patients with end-stage kidney disease whilst receiving haemodialysis.
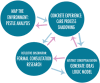
Methods: The development process utilised the Arts in Health framework (Fancourt, 2017). The framework was addressed through the establishment of an interdisciplinary advisory group, collaboration and consultation with stakeholders, a scoping and realist review, shadowing of artists-in-residence, personal arts practice and logic modelling.
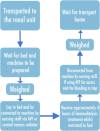
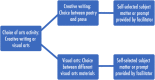
Results: The intervention involved six 1-h long, one-to-one facilitated sessions focused on creative writing and visual art. Patients could choose between art form and self-select a subject matter. The sessions had a primary focus on skill development and were delivered using principles derived from the psychological theory of flow.
Conclusion: The Arts in Health framework provided an appropriate and pragmatic approach to intervention development. Complex arts-based interventions can be developed for the purpose of evaluation within a trial framework. This intervention was designed to strike a balance between standardised components, and a person-centred approach necessary to address existential boredom.
Keywords: Arts in health; Arts-based intervention; Chronic disease; End-stage kidney disease; Haemodialysis; Intervention development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Registry UR: UK Renal Registry 22nd Annual Report - data to 31/12/2018. In. Bristol, UK; 2020.
-
- van der Willik EM, Hemmelder MH, Bart HA, van Ittersum FJ, Hoogendijk-van den Akker JM, Bos WJW, Dekker FW, Meuleman Y: Routinely measuring symptom burden and health-related quality of life in dialysis patients: first results from the Dutch registry of patient-reported outcome measures. Clinical Kidney Journal 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bublitz L, Hiremagalur B, Purtell L, Sowa M, Gillespie K, Bonner A: 33. Tracking patient-reported symptoms in people undergoing dialysis: the LEOPARD study. Renal Society of Australasia Journal 2018, 14:29-29.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical