Adjuvant effects of vitamin A and vitamin D supplementation on treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a study protocol for a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicentric trial in China
- PMID: 34135055
- PMCID: PMC8211063
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-050541
Adjuvant effects of vitamin A and vitamin D supplementation on treatment of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a study protocol for a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multicentric trial in China
Abstract
Introduction: Approximately 7.2% of children in the world suffer from attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Due to the availability of the osmotic-release oral-system methylphenidate, ADHD currently has a remission rate of up to 30.72%. Nevertheless, it has been reported that patients with ADHD tend to exhibit vitamin A and vitamin D deficiency, which may aggravate the symptoms of ADHD. This study aims to determine the effect of vitamin A and vitamin D supplementation as adjunctive therapy to methylphenidate on the symptoms of ADHD.
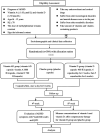
Methods and analysis: This is a parallel, prospective, interventional multicentric study. Patients will be enrolled from the southern, central and northern parts of China. A target of 504 patients will be followed for 8 weeks. They will be allocated into three groups (vitamin AD, vitamin D and placebo) and administered the interventions accordingly. Data on changes in the symptoms of ADHD as well as changes in the serum concentrations of vitamin A and vitamin D will be recorded. Both responders and nonresponders based on the sociodemographic and clinical data will also be described to mitigate selection bias.
Ethics and dissemination: This study is performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, China (approval number: (2019) IRB (STUDY) number 262). The results of the trial will be reported in peer-reviewed scientific journals and academic conferences regardless of the outcomes.
Trial registration number: NCT04284059.
Keywords: neurobiology; paediatrics; protocols & guidelines; public health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019 Nov;29(9):670-687. doi: 10.1089/cap.2019.0059. Epub 2019 Aug 1. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31368773
-
Effect of vitamin D supplementation as adjunctive therapy to methylphenidate on ADHD symptoms: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial.Nutr Neurosci. 2018 Apr;21(3):202-209. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2016.1262097. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Nutr Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 27924679 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Acute Comparator Trials of Lisdexamfetamine and Extended-Release Methylphenidate in Adolescents With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder.CNS Drugs. 2017 Nov;31(11):999-1014. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0468-2. CNS Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28980198 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate treatment of adult male prison inmates with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial with open-label extension.Br J Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;200(1):68-73. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.111.092940. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Br J Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22075648 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy and acceptability of atomoxetine, lisdexamfetamine, bupropion and methylphenidate in treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis with focus on bupropion.J Affect Disord. 2015 Jun 1;178:149-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 13. J Affect Disord. 2015. PMID: 25813457 Review.
Cited by
-
Parents' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding vitamin A and D intake in children: a study from Yangzhou, China.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 20;25(1):700. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-21920-3. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39979933 Free PMC article.
-
Eating Patterns and Dietary Interventions in ADHD: A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 16;14(20):4332. doi: 10.3390/nu14204332. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36297016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of multivitamins on neurological and growth disorders: a cross-sectional study.Front Nutr. 2024 Sep 25;11:1465875. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1465875. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39385784 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and the Central Nervous System: Causative and Preventative Mechanisms in Brain Disorders.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 17;14(20):4353. doi: 10.3390/nu14204353. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36297037 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tzang R-F, Wang Y-C, Yeh C-B, et al. . Naturalistic exploration of the effect of osmotic release oral system-methylphenidate on remission rate and functional improvement in Taiwanese children with attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2012;66:53–63. 10.1111/j.1440-1819.2011.02289.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical