MHC Class II Presentation Is Affected by Polymorphism in the H2-Ob Gene and Additional Loci
- PMID: 34135064
- PMCID: PMC8674376
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100061
MHC Class II Presentation Is Affected by Polymorphism in the H2-Ob Gene and Additional Loci
Abstract
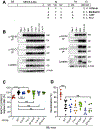
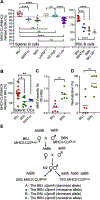
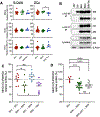
Pathogen-derived peptides are loaded on MHC class II (MHCII) and presented to CD4+ T cells for their activation. Peptide loading of MHCII occurs in specialized endosomal compartments and is controlled by the nonclassical MHCII molecules H2-M and H2-O, which are both constitutive αβ heterodimers. H2-M catalyzes MHCII peptide loading, whereas H2-O modulates H2-M activity by acting as an MHCII mimic. Recently, we discovered that the H2-Ob allele inherited by retrovirus-resistant I/LnJ mice results in nonfunctional H2-O. I/LnJ H2-O binds to but does not inhibit H2-M. Compared with H2-Oβ from virus-susceptible mice, H2-Oβ from I/LnJ mice has four unique amino acid substitutions, three in the Ig domain and one in the cytoplasmic tail. In this study we show that the three amino acids in the Ig domain of I/LnJ Oβ are critical for the H2-O inhibitory activity of H2-M. Unexpectedly, we found that MHCII presentation was significantly different in Ag-presenting cells from two closely related mouse strains, B6J and B6N, which carry identical alleles of MHCII, H2-O, and H2-M. Using a positional cloning approach, we have identified two loci, polymorphic between B6J and B6N, that mediate the difference in MHCII presentation. Collectively, these studies reveal extra complexity in MHCII/H2-M/H-2O interactions that likely involve yet to be identified modulators of the pathway.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
H2-M, a facilitator of MHC class II peptide loading, and its negative modulator H2-O are differentially expressed in response to proinflammatory cytokines.Immunogenetics. 2000 Aug;51(10):794-804. doi: 10.1007/s002510000210. Immunogenetics. 2000. PMID: 10970094
-
H2-O, a MHC class II-like protein, sets a threshold for B-cell entry into germinal centers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Sep 21;107(38):16607-12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004664107. Epub 2010 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20807742 Free PMC article.
-
TLR agonists downregulate H2-O in CD8alpha- dendritic cells.J Immunol. 2011 Oct 15;187(8):4151-60. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003137. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21918198 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting nonclassical HLA II functions in antigen presentation: Peptide editing and its modulation.HLA. 2020 Oct;96(4):415-429. doi: 10.1111/tan.14007. Epub 2020 Aug 27. HLA. 2020. PMID: 32767512 Review.
-
The role of H2-O and HLA-DO in major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted antigen processing and presentation.Immunol Rev. 1999 Dec;172:255-66. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1999.tb01370.x. Immunol Rev. 1999. PMID: 10631951 Review.
Cited by
-
A human gut Faecalibacterium prausnitzii fatty acid amide hydrolase.Science. 2024 Oct 25;386(6720):eado6828. doi: 10.1126/science.ado6828. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Science. 2024. PMID: 39446943 Free PMC article.
-
The MHC Class II Antigen-Processing and Presentation Pathway Is Dysregulated in Type 1 Diabetes.J Immunol. 2023 Dec 1;211(11):1630-1642. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300213. J Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37811896 Free PMC article.
-
CXCL16 knockout inhibit asthma airway inflammation by suppressing H2-DM molecular mediated antigen presentation.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 6;11(1):90. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02371-6. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40050290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Case LK, Purdy A, and Golovkina TV. 2005. Molecular and cellular basis of the retrovirus resistance in I/LnJ mice. J Immunol 175: 7543–7549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

