Interaction of schizophrenia and chronic cannabis use on reward anticipation sensitivity
- PMID: 34135344
- PMCID: PMC8209034
- DOI: 10.1038/s41537-021-00163-2
Interaction of schizophrenia and chronic cannabis use on reward anticipation sensitivity
Abstract
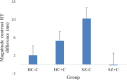
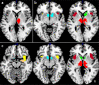
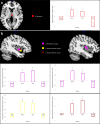
Chronic cannabis use and schizophrenia are both thought to affect reward processing. While behavioural and neural effects on reward processing have been investigated in both conditions, their interaction has not been studied, although chronic cannabis use is common among these patients. In the present study eighty-nine participants divided into four groups (control chronic cannabis users and non-users; schizophrenia patient cannabis users and non-users) performed a two-choice decision task, preceded by monetary cues (high/low reward/punishment or neutral), while being scanned using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Reward and punishment anticipation resulted in activation of regions of interest including the thalamus, striatum, amygdala and insula. Chronic cannabis use and schizophrenia had opposing effects on reward anticipation sensitivity. More specifically control users and patient non-users showed faster behavioural responses and increased activity in anterior/posterior insula for high magnitude cues compared to control non-users and patient users. The same interaction pattern was observed in the activation of the right thalamus for reward versus punishment cues. This study provided evidence for interaction of chronic cannabis use and schizophrenia on reward processing and highlights the need for future research addressing the significance of this interaction for the pathophysiology of these conditions and its clinical consequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Alterations of monetary reward and punishment processing in chronic cannabis users: an FMRI study.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 23;10(3):e0119150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119150. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25799565 Free PMC article.
-
Increased ventral striatal BOLD activity during non-drug reward anticipation in cannabis users.Neuroimage. 2010 Jan 1;49(1):1133-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.07.022. Epub 2009 Jul 23. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 19631753 Free PMC article.
-
Neural responses to reward anticipation and feedback in adult and adolescent cannabis users and controls.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022 Oct;47(11):1976-1983. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01316-2. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35388175 Free PMC article.
-
Brain reward function in people who use cannabis: a systematic review.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Feb 6;17:1323609. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1323609. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38379938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging the "social brain" in schizophrenia: A systematic review of neuroimaging studies of social reward and punishment.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020 Nov;118:704-722. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2020. PMID: 32841653
Cited by
-
Using Task-fMRI to Explore the Relationship Between Lifetime Cannabis Use and Cognitive Control in Individuals With First-Episode Schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull Open. 2024 Jul 24;5(1):sgae016. doi: 10.1093/schizbullopen/sgae016. eCollection 2024 Jan. Schizophr Bull Open. 2024. PMID: 39144106 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

