Rab10-Positive Tubular Structures Represent a Novel Endocytic Pathway That Diverges From Canonical Macropinocytosis in RAW264 Macrophages
- PMID: 34135890
- PMCID: PMC8203412
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.649600
Rab10-Positive Tubular Structures Represent a Novel Endocytic Pathway That Diverges From Canonical Macropinocytosis in RAW264 Macrophages
Abstract
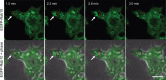
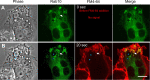
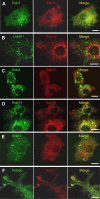
Using the optogenetic photo-manipulation of photoactivatable (PA)-Rac1, remarkable cell surface ruffling and the formation of a macropinocytic cup (premacropinosome) could be induced in the region of RAW264 macrophages irradiated with blue light due to the activation of PA-Rac1. However, the completion of macropinosome formation did not occur until Rac1 was deactivated by the removal of the light stimulus. Following PA-Rac1 deactivation, some premacropinosomes closed into intracellular macropinosomes, whereas many others transformed into long Rab10-positive tubules without forming typical macropinosomes. These Rab10-positive tubules moved centripetally towards the perinuclear Golgi region along microtubules. Surprisingly, these Rab10-positive tubules did not contain any endosome/lysosome compartment markers, such as Rab5, Rab7, or LAMP1, suggesting that the Rab10-positive tubules were not part of the degradation pathway for lysosomes. These Rab10-positive tubules were distinct from recycling endosomal compartments, which are labeled with Rab4, Rab11, or SNX1. These findings suggested that these Rab10-positive tubules may be a part of non-degradative endocytic pathway that has never been known. The formation of Rab10-positive tubules from premacropinosomes was also observed in control and phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-stimulated macrophages, although their frequencies were low. Interestingly, the formation of Rab10-positive premacropinosomes and tubules was not inhibited by phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors, while the classical macropinosome formation requires PI3K activity. Thus, this study provides evidence to support the existence of Rab10-positive tubules as a novel endocytic pathway that diverges from canonical macropinocytosis.
Keywords: Rab10; endocytosis; live-cell imaging; macrophages; macropinocytosis; tubules.
Copyright © 2021 Kawai, Nishigaki, Moriya, Egami and Araki.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dissecting the roles of Rac1 activation and deactivation in macropinocytosis using microscopic photo-manipulation.Sci Rep. 2013;3:2385. doi: 10.1038/srep02385. Sci Rep. 2013. PMID: 23924974 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 and Rab10 coordinate macropinocytosis to mediate immunological responses in phagocytes.EMBO J. 2020 Oct 15;39(20):e104862. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104862. Epub 2020 Aug 27. EMBO J. 2020. PMID: 32853409 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes in the spatiotemporal localization of Rab21 in live RAW264 cells during macropinocytosis.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 20;4(8):e6689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006689. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19693279 Free PMC article.
-
Macropinocytosis: searching for an endocytic identity and role in the uptake of cell penetrating peptides.J Cell Mol Med. 2007 Jul-Aug;11(4):670-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00062.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17760832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular imaging analysis of Rab GTPases in the regulation of phagocytosis and macropinocytosis.Anat Sci Int. 2016 Jan;91(1):35-42. doi: 10.1007/s12565-015-0313-y. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Anat Sci Int. 2016. PMID: 26530641 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological Evidence for Novel Roles of Microtubules in Macrophage Phagocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 10;24(2):1373. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021373. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674886 Free PMC article.
-
Functional significance of ion channels during macropinosome resolution in immune cells.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 20;13:1037758. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1037758. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36338503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles for 3' Phosphoinositides in Macropinocytosis.Subcell Biochem. 2022;98:119-141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-94004-1_7. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35378706 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella exploits membrane reservoirs for invasion of host cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 10;15(1):3120. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47183-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38600106 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella exploits LRRK2-dependent plasma membrane dynamics to invade host cells.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 8;16(1):2329. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57453-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40057496 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sallusto F, Cella M, Danieli C, Lanzavecchia A. Dendritic Cells Use Macropinocytosis and the Mannose Receptor to Concentrate Macromolecules in the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Compartment: Downregulation by Cytokines and Bacterial Products. J Exp Med (1995) 182:389–400. 10.1084/jem.182.2.389 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

