Single-Cell Profiling Reveals Transcriptional Signatures and Cell-Cell Crosstalk in Anti-PLA2R Positive Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy Patients
- PMID: 34135910
- PMCID: PMC8202011
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.683330
Single-Cell Profiling Reveals Transcriptional Signatures and Cell-Cell Crosstalk in Anti-PLA2R Positive Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy Patients
Abstract
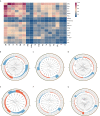
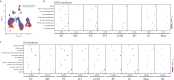
Idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) is an organ-specific autoimmune disease of the kidney glomerulus. It may gradually progress to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) characterized by increased proteinuria, which leads to serious consequences. Although substantial advances have been made in the understanding of the molecular bases of IMN in the last 10 years, certain questions remain largely unanswered. To define the transcriptomic landscape at single-cell resolution, we analyzed kidney samples from 6 patients with anti-PLA2R positive IMN and 2 healthy control subjects using single-cell RNA sequencing. We then identified distinct cell clusters through unsupervised clustering analysis of kidney specimens. Identification of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and enrichment analysis as well as the interaction between cells were also performed. Based on transcriptional expression patterns, we identified all previously described cell types in the kidney. The DEGs in most kidney parenchymal cells were primarily enriched in genes involved in the regulation of inflammation and immune response including IL-17 signaling, TNF signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling, and MAPK signaling. Moreover, cell-cell crosstalk highlighted the extensive communication of mesangial cells, which infers great importance in IMN. IMN with massive proteinuria displayed elevated expression of genes participating in inflammatory signaling pathways that may be involved in the pathogenesis of the progression of IMN. Overall, we applied single-cell RNA sequencing to IMN to uncover intercellular interactions, elucidate key pathways underlying the pathogenesis, and identify novel therapeutic targets of anti-PLA2R positive IMN.
Keywords: idiopathic membranous nephropathy; immune response; inflammation; kidney; single-cell RNA sequence.
Copyright © 2021 Xu, Shen, Lin, Meng, Ooi, Eggenhuizen, Tang, Xiao, Jin, Ding, Tang, Peng, Nie, Ao, Xiao, Zhong and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical value of renal phospholipase A2 receptor deposit in the prognosis evaluation and treatment options of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A retrospective cohort study.Nephrology (Carlton). 2020 Mar;25(3):219-229. doi: 10.1111/nep.13691. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Nephrology (Carlton). 2020. PMID: 31900967 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Histological Features of Phospholipase A2 Receptor-Associated and Thrombospondin Type-I Domain-containing 7A-Associated Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy: A Single Center Retrospective Study from China.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jul 22;24:5076-5083. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909815. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30032157 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic specificity of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) in differentiating idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN) from secondary forms and other glomerular diseases.J Nephrol. 2018 Apr;31(2):271-278. doi: 10.1007/s40620-017-0451-5. Epub 2017 Oct 28. J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29081027
-
Clinical usefulness of autoantibodies to M-type phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) for monitoring disease activity in idiopathic membranous nephropathy (IMN).Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Feb;15(2):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.004. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2016. PMID: 26527329 Review.
-
[Anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (anti-PLA2R) antibodies and idiopathic membranous nephropathy: which role in diagnosis and prognosis of this disease?].G Ital Nefrol. 2014 May-Jun;31(3):gin/31.3.13. G Ital Nefrol. 2014. PMID: 25030016 Review. Italian.
Cited by
-
C3aR-initiated signaling is a critical mechanism of podocyte injury in membranous nephropathy.JCI Insight. 2024 Jan 16;9(4):e172976. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172976. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 38227377 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of Medications for Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy Using Glomerular Whole-Genome Sequencing.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 14;2022:9337088. doi: 10.1155/2022/9337088. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 35465008 Free PMC article.
-
Intrarenal Single-Cell Sequencing of Hepatitis B Virus Associated Membranous Nephropathy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:869284. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.869284. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35935760 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: Potential mediators between particulate matter 2.5 and Th17/Treg immune disorder in primary membranous nephropathy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 21;13:968256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.968256. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210816 Free PMC article.
-
Membranous nephropathy with systemic light-chain amyloidosis of remission after rituximab therapy: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Aug 16;11(23):5538-5546. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i23.5538. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37637680 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

