Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM) Injection Ameliorates Iron Overload-Associated Cardiac Dysfunction by Regulating the Expression of DMT1, TfR1, and FP1 in Rats
- PMID: 34135983
- PMCID: PMC8175163
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6864723
Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM) Injection Ameliorates Iron Overload-Associated Cardiac Dysfunction by Regulating the Expression of DMT1, TfR1, and FP1 in Rats
Abstract
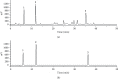
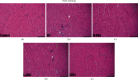
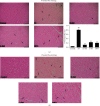
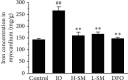
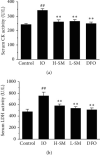
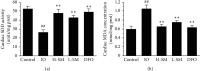
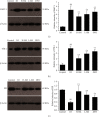
Previous studies have found that Salvia miltiorrhiza (SM) injection have a protective effect on the iron overloaded (IO) heart. However, the mechanisms are not completely known. In the present study, we investigated the underlying mechanisms based on the iron transport-related proteins. The rats were randomly divided into five groups: control, IO group, low-dose SM group, high-dose SM group, and deferoxamine control group. Iron dextran was injected to establish the IO model. After 14 days of treatment, cardiac histological changes were observed by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Iron uptake-related proteins divalent metal transporter-1 (DMT-1), transferrin receptor-1 (TfR-1), and iron export-related proteins ferroportin1 (FP1) in the heart were detected by Western blotting. The results showed that SM injection decreased cardiac iron deposition, ameliorated cardiac function, and inhibited cardiac oxidation. Most important of all, SM injection downregulated the expression of DMT-1 and TfR-1 and upregulated FP1 protein levels compared with the IO group. Our results indicated that reducing cardiac iron uptake and increasing iron excretion may be one of the important mechanisms of SM injection reducing cardiac iron deposition and improving cardiac function under the conditions of IO.
Copyright © 2021 Yuanyuan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multitargeted inhibition of hepatic fibrosis in chronic iron-overloaded mice by Salvia miltiorrhiza.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 9;148(2):671-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.028. Epub 2013 May 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23707206
-
Continuing treatment with Salvia miltiorrhiza injection attenuates myocardial fibrosis in chronic iron-overloaded mice.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0124061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124061. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25850001 Free PMC article.
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) injection ameliorates iron overload-induced cardiac damage in mice.Planta Med. 2013 Jun;79(9):744-52. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1328588. Epub 2013 May 22. Planta Med. 2013. PMID: 23700113
-
Mechanisms and regulation of intestinal iron absorption.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2002 Nov-Dec;29(3):384-99. doi: 10.1006/bcmd.2002.0578. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2002. PMID: 12547229 Review.
-
Divalent metal transporter 1.Hematology. 2005 Aug;10(4):339-45. doi: 10.1080/10245330500093419. Hematology. 2005. PMID: 16085548 Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration of osteoclast activity in childhood cancer survivors: Role of iron and of CB2/TRPV1 receptors.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 21;17(7):e0271730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271730. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35862357 Free PMC article.
-
TFR1 knockdown alleviates iron overload and mitochondrial dysfunction during neural differentiation of Alzheimer's disease-derived induced pluripotent stem cells by interacting with GSK3B.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Feb 6;29(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01677-y. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38321571 Free PMC article.
-
Roots of Astragalus propinquus Schischkin Regulate Transmembrane Iron Transport and Ferroptosis to Improve Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 2;2022:7410865. doi: 10.1155/2022/7410865. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35958925 Free PMC article.
-
The underlying pathological mechanism of ferroptosis in the development of cardiovascular disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 8;9:964034. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.964034. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36003910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron overload impairs renal function and is associated with vascular calcification in rat aorta.Biometals. 2022 Dec;35(6):1325-1339. doi: 10.1007/s10534-022-00449-7. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Biometals. 2022. PMID: 36178540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Milman N., Pedersen P., Steig T. Á., Byg K.-E., Graudal N., Fenger K. Clinically overt hereditary hemochromatosis in Denmark 1948–1985: epidemiology, factors of significance for long-term survival, and causes of death in 179 patients. Annals of Hematology. 2001;80(12):737–744. doi: 10.1007/s002770100371. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

