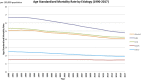
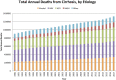
Global Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease
- PMID: 34136143
- PMCID: PMC8177826
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.1061
Global Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease
Figures
References
-
- Global Health Estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. Available at: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/estimates/en/. Accessed June 15, 2020.
-
- Asrani SK, Devarbhavi H, Eaton J, Kamath PS. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J Hepatol 2019;70:151‐171. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources