The Prognosis and Oncological Predictor of Urachal Carcinoma of the Bladder: A Large Scale Multicenter Cohort Study Analyzed 203 Patients With Long Term Follow-Up
- PMID: 34136407
- PMCID: PMC8202399
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.683190
The Prognosis and Oncological Predictor of Urachal Carcinoma of the Bladder: A Large Scale Multicenter Cohort Study Analyzed 203 Patients With Long Term Follow-Up
Abstract
Aim: This study evaluated the prognosis and survival predictors for bladder urachal carcinoma (UC), based on large scale multicenter cohort with long term follow-up database.
Methods: A total 203 patients with bladder UC treated at 19 hospitals were enrolled. Clinical parameters on carcinoma presentation, diagnosis, and therapeutic methods were reviewed for the primary cancer and for all subsequent recurrences. The stage of UC was stratified by Mayo and Sheldon pathological staging system. Oncological outcomes and the possible clinicopathological parameters associated with survival outcomes were investigated.
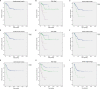
Results: The mean age of the patients was 54.2 years. Among the total of 203 patients, stages I, II, III, and IV (Mayo stage) were 48 (23.8%), 108 (53.5%), 23 (11.4%), and 23 (11.4%), respectively. Gross hematuria and bladder irritation symptoms were the two most common initial symptoms. The mean follow-up period was 65 months, and 5-year overall survival rates (OS), cancer-specific survival rates (CSS), and recurrence-free survival rates (RFS) were 88.3, 83.1, and 63.9%, respectively. For the patients with Mayo stage ≥III, OS, CSS, and RFS were significantly decreased to 38.0, 35.2, and 28.4%, respectively. The higher pathological stage (Mayo stage ≥III, Sheldon stage ≥IIIc), positive surgical margin (PSM), and positive lymphovascular invasion (PLM) were independent predictors of shorter OS, CSS, and RFS.
Conclusion: The pathological stage, PSM, and PLM were significantly associated with the survival of UC patients, emphasizing an importance of the complete surgical resection of tumor lesion.
Keywords: bladder; lymphovascular invasion; surgical margin; survival rate; urachal carcinoma.
Copyright © 2021 Yu, Ko, Kim, Jung, Kang, Park, Seo, Kim, Jeong, Kim, Choi, Nam, Ku, Joo, Jang, Yoon, Yun, Hong and Oh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mennitto A, Vernieri C, Procopio G. Urachal Carcinoma: Towards a Precision Medicine. Transl Cancer Res (2016) 5(Suppl 7):S1307. 10.21037/tcr.2016.12.28 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

