Mammography with a fully automated breast volumetric software as a novel method for estimating the preoperative breast volume prior to mastectomy
- PMID: 34136427
- PMCID: PMC8176198
- DOI: 10.4174/astr.2021.100.6.313
Mammography with a fully automated breast volumetric software as a novel method for estimating the preoperative breast volume prior to mastectomy
Abstract
Purpose: Increasing interest in maintaining a positive body image following breast cancer surgery has become an important aspect of reconstruction surgery. Volume matching of the reconstructed breast to natural breasts is the most important consideration. This study aimed to explore the feasibility of using mammography with a fully automated breast volumetric software to measure the preoperative breast volume in patients with breast cancer.
Methods: We evaluated patients who underwent a total mastectomy between July 2016 and February 2021. The specimen volume following total mastectomy was compared with breast volume estimates using a fully automated volumetric software (Quantra ver. 2.1.1) and 4 other previously described mammography-based prediction methods. The association between the estimates and mastectomy specimen volume was assessed using Pearson correlation and Bland-Altman analysis.
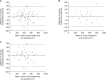
Results: Sixty-six patients were included. Compared with previously described mammography-based methods, Quantra estimates were more strongly correlated with mastectomy specimen volume in the entire, fatty, and dense breast groups (r = 0.920, 0.921, and 0.915, respectively; P < 0.001). In applying Quantra estimates for measuring preoperative breast volume, we adjusted a simple equation: mastectomy specimen volume = Quantra estimate × 0.8.
Conclusion: Mammography with a fully automated breast volumetric software can be useful for measuring preoperative breast volume in patients with breast cancer who undergo reconstruction surgery.
Keywords: Breast density; Breast neoplasms; Mammography; Mastectomy; Organ size; Software.
Copyright © 2021, the Korean Surgical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated Breast Volume Assessment Derived From Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Images Compared to Mastectomy Specimen Weight and Its Applications in Cosmetic Optimisation.Cureus. 2021 Nov 16;13(11):e19642. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19642. eCollection 2021 Nov. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34926087 Free PMC article.
-
Automated Volumetric Mammographic Breast Density Measurements May Underestimate Percent Breast Density for High-density Breasts.Acad Radiol. 2017 Dec;24(12):1561-1569. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.06.002. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Acad Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28754209
-
Comparing Visually Assessed BI-RADS Breast Density and Automated Volumetric Breast Density Software: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Breast Cancer Screening Setting.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 3;10(9):e0136667. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136667. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26335569 Free PMC article.
-
Calculation of breast volumes from mammogram: Comparison of four separate equations relative to mastectomy specimen volumes.J Surg Oncol. 2018 Jun;117(8):1848-1853. doi: 10.1002/jso.25076. Epub 2018 May 22. J Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29790170
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of correlation of automated breast density measurement.Radiography (Lond). 2024 Aug;30(5):1455-1467. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2024.08.003. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Radiography (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39164186
Cited by
-
Clinical use of perioperative magnetic resonance imaging-based breast volumetric analysis in final implant volume prediction for two-stage breast reconstruction.Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022 Oct;103(4):195-204. doi: 10.4174/astr.2022.103.4.195. Epub 2022 Oct 7. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2022. PMID: 36304192 Free PMC article.
-
How Reliable Is Breast Volume Assessment When the Patient Is Lying Flat?-Volumetric Assessment of Breast Volume Using a Vectra H2 Handheld Device in Different Positions.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):709. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030709. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Utsunomiya H, Kusano T, Sato N, Yoshimoto S. Estimating implant volume and mastectomy-specimen volume by measuring breast volume with a 3-dimensional scanner. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;79:79–81. - PubMed
-
- Choppin SB, Wheat JS, Gee M, Goyal A. The accuracy of breast volume measurement methods: a systematic review. Breast. 2016;28:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs L, Eder M, Hol lweck R, Zimmermann A, Settles M, Schneider A, et al. Comparison between breast volume measurement using 3D surface imaging and classical techniques. Breast. 2007;16:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Yip JM, Mouratova N, Jeffery RM, Veitch DE, Woodman RJ, Dean NR. Accurate assessment of breast volume: a study comparing the volumetric gold standard (direct water displacement measurement of mastectomy specimen) with a 3D laser scanning technique. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;68:135–141. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

