Diabetic Endothelial Cells Differentiated From Patient iPSCs Show Dysregulated Glycine Homeostasis and Senescence Associated Phenotypes
- PMID: 34136485
- PMCID: PMC8201091
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.667252
Diabetic Endothelial Cells Differentiated From Patient iPSCs Show Dysregulated Glycine Homeostasis and Senescence Associated Phenotypes
Abstract
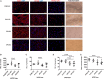
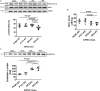
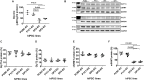
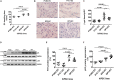
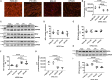
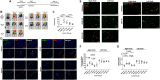
Induced pluripotent stem cells derived cells (iPSCs) not only can be used for personalized cell transfer therapy, but also can be used for modeling diseases for drug screening and discovery in vitro. Although prior studies have characterized the function of rodent iPSCs derived endothelial cells (ECs) in diabetes or metabolic syndrome, feature phenotypes are largely unknown in hiPSC-ECs from patients with diabetes. Here, we used hiPSC lines from patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and differentiated them into ECs (dia-hiPSC-ECs). We found that dia-hiPSC-ECs had disrupted glycine homeostasis, increased senescence, and impaired mitochondrial function and angiogenic potential as compared with healthy hiPSC-ECs. These signature phenotypes will be helpful to establish dia-hiPSC-ECs as models of endothelial dysfunction for understanding molecular mechanisms of disease and for identifying and testing new targets for the treatment of endothelial dysfunction in diabetes.
Keywords: endothelial function; endothelium; glycine; mitochondrial function; senescence.
Copyright © 2021 Su, Kong, Loo, Gao, Kovalik, Su, Ma and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Christensen K., Roudnicky F., Burcin M., Patsch C. (2019). Monolayer generation of vascular endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994 17–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

